Hesperian Health Guides
What Causes Infertility?
HealthWiki > Where Women Have No Doctor > Chapter 14: Infertility (When You Are Not Able to Have a Baby) > What Causes Infertility?
- Few sperm are produced, or the sperm produced cannot fertilize an egg, possibly because of:
- genetic or developmental problems.
- smoking tobacco, drinking a lot of alcohol, or using drugs.
- exposure to toxic chemicals.
- malnutrition or diabetes.
- The testicles are damaged or work differently, possibly because of:
- illnesses like tuberculosis, mumps, or untreated STIs.
- physical injuries.
- a condition called varicocele that reduces blood flow to a testicle.
- changes in hormones, which affect sperm production.
- The penis cannot deliver sperm to the vagina, possibly because of:
- conditions that make ejaculation difficult or impossible, such as diabetes or spinal cord injury, or a penis that doesn’t get hard during sex.
- an STI that damaged the tubes that carry the semen and sperm.
Problems with the egg, the womb, or the tubes can all lead to infertility. These problems can have a variety of causes.
Infertility caused by infection can be prevented. See Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and How to Prevent STIs.
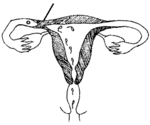
| blocked tube |
 |
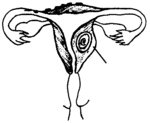 fibroid |
- An egg is not produced, or an egg produced cannot develop into a fetus after fertilization, possibly because of:
- genetic problems.
- having very low or very high body fat, which affects the hormones that control ovulation.
- smoking tobacco, drinking a lot of alcohol, or using drugs
- The womb is damaged or works differently, possibly because of:
- growths in the womb (like fibroids) that prevent pregnancy.
- scarring from an untreated STI, an infection after birth, or an unsafe abortion, which blocks sperm from reaching the egg or prevents a fertilized egg from attaching to the womb.
- differences in womb shape.
- changes in hormones that affect the womb’s lining.
- The tubes stop sperm from reaching an egg, possibly because of:
- illnesses like tuberculosis or untreated STIs that damage the tubes and block the sperm.
This page was updated:29 May 2025
Sources
- Guzick, et al. (2001) Sperm Morphology, Motility, and Concentration in Fertile and Infertile Men
- UpToDate (2022) Causes of Female Infertility
- UpToDate (2020) Causes of Male Infertility
- UpToDate (2022) Patient education: Female infertility (The Basics)
- UpToDate (2022) Natural fertility and impact of lifestyle factors