Hesperian Health Guides
Hormonal Methods of Family Planning
HealthWiki > Where Women Have No Doctor > Chapter 13: Family Planning > Hormonal Methods of Family Planning
| 
|
| 
|
| 
|
Hormonal methods are controlled by the person who can become pregnant, and they can be used without partners knowing.
Hormonal methods work by making mucus in the cervix so thick it stops sperm, and by keeping the lining of the womb very thin. Some stop the egg from being released.
Most birth control pills, patches, vaginal rings, and some injections contain both estrogen and progestin. These are called “combined” hormonal methods and are very effective. Some people should not use methods with estrogen or any hormonal method (see below).
Implants, some intrauterine devices (IUDs), some injections, and some pills contain only progestin. These are also effective and are safe for people who cannot use methods with estrogen.
Some medicines for seizures, migraines, or tuberculosis (TB) make hormonal methods less effective. If you take these medicines, use a different family planning method or combine your hormonal method with another method, such as a condom or a diaphragm.
Contents
- 1 Do not use ANY hormonal method if:
- 2 Do not use methods that contain estrogen if:
- 3 Side effects of hormonal methods
- 4 Combined pills (pills that contain estrogen and progestin)
- 5 The patch and the vaginal ring
- 6 Minipills (pills that contain only progestin)
- 7 Implants (Implanon, Jadelle, Levoplant, Nexplanon, Sino-implant)
- 8 Injectable contraceptives
Do not use ANY hormonal method if:
 |
| ||
 |
| ||
If you have other health problems and want to use a hormonal method, talk to a health worker who has been trained in them.
Do not use methods that contain estrogen if:
- you have any of the conditions listed above.
- you have high blood pressure that is not controlled by medicine.
- you have had diabetes for 20 years, or have kidney, eye, or nerve problems from diabetes.
- you have liver disease, hepatitis, or yellow skin and eyes.
- you have ever had a blood clot in a vein (signs: swelling and pain in a leg).
- you get migraine headaches, especially with vision changes.
- you smoke and are 35 years old or older, to avoid more risk of heart attack or stroke.
- you gave birth in the last 6 weeks.
Estrogen can reduce breast milk, so if you are breastfeeding you might avoid methods with estrogen for at least 6 months.
Combined pills (pills that contain estrogen and progestin)
If you are bothered by any changes in your body after starting birth control pills, talk to a health worker. They might suggest a different pill or another method
If you are given a new medicine while on combined pills, ask your health worker if you should use a barrier method or not have sex while taking the medicine. Some medicines make combined pills less effective.
Combined pills are usually available at family planning clinics, health posts, and pharmacies, and through health workers. There are many brands of combined pills with different types and amounts of estrogen and progestin in them. Most have 35 micrograms (mcg) of estrogen or less.
Once you start taking pills, try to use the same brand (and if you can, buy several packets at once). If you must change brands, try to get another with the same hormone names and amounts. This will cause fewer side effects
Common side effects of combined pills:
- Changes in bleeding. The most common side effect of combined pills is that periods become shorter and lighter. It is also normal to sometimes skip a period. You may also have spotting (bleeding at other times than your normal period). To reduce spotting, take your pill at the same time every day.
- Nausea (the feeling that you might throw up). This usually goes away after a few months. If it bothers you, try taking your pill with food or just before going to sleep at night.
- Headaches. Mild headaches in the first few months are common. Pain medicine such as ibuprofen or paracetamol (acetaminophen) should help. If the headache is severe or comes with blurred eyesight, this could be a serious warning sign, see below.
How to take combined birth control pills:
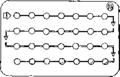
| Most combined pills come in packets of 21 or 28 tablets. If you have a 28-day packet, take one pill every day. As soon as you finish one packet, start taking pills from a new packet. The last 7 pills in a 28-day packet have no hormones in them. These “sugar pills” help you remember to take a pill every day. |
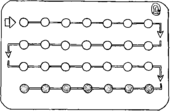 |
| 28-Day Pill Packet | |
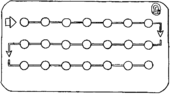 |
If you have a 21-day packet, take a pill every day for 21 days, then wait 7 days before starting a new packet. Your period will usually happen during the days you are not taking pills. But start a new packet after 7 days even if your period has not come. |
| 21-Day Pill Packet | |
| If you are sure you are not pregnant, you can start using the pill at any time during your cycle. If you start on the first day of your period, you will be protected from pregnancy right away. If you start on another day of your cycle, you will not be protected right away. So for the first 7 days you are taking the pill, use condoms or another barrier method if you have sex that can cause pregnancy.
|
|
Warning signs for problems with combined pills:
STOP taking the pill and see a health worker if you:
- have severe headaches with blurred vision (migraines) that begin after you start taking combined pills.
- feel weakness or numbness in your arms or legs.
- feel severe pain in your chest and shortness of breath.
- have severe pain in one leg.
- have severe pain in the abdomen.
If you have any of these problems, pregnancy can also be dangerous, so use another type of family planning such as condoms until you can see a health worker trained in hormonal family planning methods.
 |

If you forget to take pills, you could get pregnant
If you forget 1 pill, take that pill as soon as you remember Then take your next pill at the regular time This may mean that you take 2 pills in one day.
If you vomit or have severe diarrhea within 24 hours after taking your pill, treat this as a missed pill.
Late or missed pills may cause some bleeding, like a very light menstrual period
If you forget to take 2 or more pills in a row, take the most recent pill as soon as you remember, and discard any other missed pills. Then take the remaining pills in the pack at the regular time, even if this means taking 2 pills in one day. If you forget to take any of the last 7 hormone-containing pills in either kind of pack, finish those pills and skip the sugar pills or the 7-day waiting time and start a new pack right away.
To prevent pregnancy, use condoms or another barrier method every time you have sex that can cause pregnancy until you have taken hormone-containing pills for 7 days in a row.
To help you remember to take your pill, try taking a pill when you do a daily task, like preparing the evening meal. Or take the pill when you see the sun go down or before you sleep. Keep the packet where you can see it every day. If you still forget to take your pills often (more than once a month), think about changing to a a different kind of method.
Stopping combined pills:
If you want to change methods or get pregnant, stop taking the pills at any time. You can get pregnant right after you stop. If you do not want to get pregnant, use another birth control method right away. Most people who stop taking pills will get pregnant within their first year of trying.
 |
 |
The patch and the vaginal ring
If you often forget to take your pill, you may be able to use the birth control patch or vaginal ring instead. They prevent pregnancy with the same hormones as combined pills and have similar side effects and warning signs (see above). The patch is changed once a week, and the vaginal ring only once a month.
Minipills (pills that contain only progestin)
 |
| The minipill is safe and effective during breastfeeding. |
Minipills are safe for anyone who cannot use methods with estrogen. There are many brands of minipills with different types and amounts of progestin in them, usually available at family planning clinics, health posts, pharmacies, and through health workers.
Do not use the minipill if you should not use hormonal methods for health reasons or if you are taking medicine for seizures or tuberculosis (TB), because these medicines make the minipill less effective.
Common side effects of the minipill:
The most common side effect is bleeding at different times from your normal period. Taking your pill at the same time every day may lessen this. It may also help to take 400 to 800 mg of ibuprofen, 3 times a day for 5 to 10 days. Your periods may also become shorter and lighter or sometimes skip completely.
How to take minipills:
If you are sure you are not pregnant, you can start using the minipill at any time. If you start on the first day of your period, you will be protected from pregnancy right away. If you start on another day of your cycle (or if you are breastfeeding and your period has not returned), you will not be protected right away. So for the first 2 days you are taking the minipill, use condoms or another barrier method if you have sex that can cause pregnancy. When you finish a packet, start your new packet the next day, even if you have not had any bleeding. Do not skip a day. Take the pill at the same time every day. If you take the pill even a few hours late, or if you forget to take the pill for only one day, you can become pregnant.
What to do if you miss a minipill, or take it more than 3 hours late:
Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at the regular time, even if it means taking 2 pills in one day. Use a barrier method or do not have sex for the next 2 days. If you vomit or have severe diarrhea within 4 hours after taking your pill, treat this as a missed pill. If you do not have a period during a cycle where you missed a pill or took it late, you may want to get a pregnancy test.
Stopping minipills:
You can stop taking minipills any time. You can get pregnant the day after you stop, so use another method right away if you do not want to become pregnant.
Implants (Implanon, Jadelle, Levoplant, Nexplanon, Sino-implant)
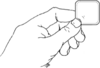
|
Implants are small, soft tubes that are placed under the skin on the inside of your arm. These tubes release the hormone progestin and prevent pregnancy similarly to minipills. They work for 3 to 5 years, depending on the type of implant.
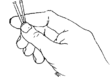
How to use implants:
A trained health worker makes a small cut in the skin to insert and remove the implants. This is usually done at a clinic or family planning center.
Contraceptive implants are one of the most effective birth control methods available.
Implants can be used by people who cannot use methods that contain estrogen. Do not use implants if you should not use any hormonal method. If you are taking medicines for seizures and certain medicines for HIV, use condoms or another barrier method every time you have sex that can cause pregnancy. These medicines make implants less effective.
Common side effects of implants:
The most common side effects of implants are changes in bleeding. You may have a longer period or bleed at unusual times. Or you may have no bleeding at all. This does not mean that you are pregnant or that something is wrong. If this irregular bleeding does not go away after a few months and bothers you, a health worker may have you take ibuprofen or combined birth control pills with the implants for a short period of time. Some people have their implants removed early due to irregular bleeding. You may also have occasional headaches.
To stop using implants:
Implants can be removed at any time by a health worker who knows how to remove them. After removal, you can get pregnant right away, so use another family planning method if you do not want to become pregnant.
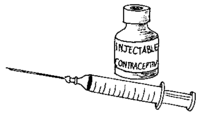
Injectable contraceptives
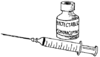
|
With this method, you get an injection to prevent pregnancy. This may happen at a health center or clinic, or you may do it yourself at home. Protection lasts 1 to 3 months depending on the type of injection, and it can be used without others knowing.
Progestin-only injections
Progestin-only injections (Depo-Provera, Sayana Press, Noristerat) have no other hormones besides progestin. These are given every 2 to 3 months, and are safe for people who cannot use methods that contain estrogen. Do not use progestin-only injections if you should not use any hormonal method.
Common side effects of progestin-only injections:
Progestin-only injections almost always cause changes in bleeding because of the large dose of progestin given in each injection. You may have light bleeding every day or every once in a while. Most irregular bleeding will stop after a few months. If irregular bleeding or heavy spotting is a problem, a health worker can give you combined birth control pills to take with the injections for a short period of time.
Some people who use progestin-only injections stop having menstrual periods by the end of the first year of use.
Some people gain weight on this method.
Combined injections
Other injections (Cyclofem and Mesigyna) contain both estrogen and progestin, and are given every month. This type of injection is much less likely to make your period stop. However, combined injections are often more expensive and harder to find than progestin-only injections.
If you cannot use methods that contain estrogen or if you should not use any hormonal method, you should not use combined injections.
Common side effects of combined injections:
Because these injections contain the same hormones as combined birth control pills, they have similar side effects.
How to use birth control injections:
If you get your first injection in the first 5 days of your period, you can be sure you are not pregnant and you will be protected from pregnancy right away. If you are sure you are not pregnant, you can get your first injection at any time during your menstrual cycle, but you will not be protected right away, so you should use condoms or another barrier method for 7 days after your first injection, or not have sex that can cause pregnancy. To stay protected, you must have an injection every 1, 2, or 3 months, depending on the kind of injection:
- Depo-Provera and Sayana Press: every 3 months
- Noristerat: every 2 months
- Cyclofem and Mesigyna: every month
To stop using injections:
You can stop having birth control injections any time you want. After you stop, it can take up to a year for your menstrual cycle to return to normal and for you to become pregnant. If you do not want to become pregnant, start using another family planning method.
Sources
- CDC (2016) U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016
- Hatcher, et al. (2018) Contraceptive Technology
- World Health Organization (2018) Family Planning: A global handbook for providers
- World Health Organization (2015) Medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use
- UpToDate (2022) Contraception: Etonogestrel implant
- World Health Organization (2015) Medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use
- Reproductive Health Access Project (2021) Quickstart Algorithm for Hormonal Contraception
- UpToDate (2022) Contraception: Progestin-only pills (POPs)
- UpToDate (2022) Evaluation and management of unscheduled bleeding in individuals using hormonal contraception
- Teunissen, et al. (2013) Continuation rates of the subdermal contraceptive Implanon® and associated influencing factors
- UpToDate (2022) Combined estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives: Patient selection, counseling, and use
- UpToDate (2022) Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA): Efficacy, side effects, metabolic impact, and benefits