Hesperian Health Guides
Abnormal Discharge
HealthWiki > Where Women Have No Doctor > Chapter 16: Sexually Transmitted Infections and Other Infections of the Genitals > Abnormal Discharge
Discharge that is clear, milky, or slightly yellow is normal. Discharge that has a bad smell, comes with itching or irritation, or is different in color or amount from usual is called “abnormal discharge” and may be a sign of an STI.

Abnormal discharge means a change in the smell, amount, or color in the fluids from your vagina compared to what is usual for you. This can mean you have an infection.
Common causes of abnormal discharge
Abnormal discharge can be a sign of a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis, which are not sexually transmitted, or a sign of trichomonas, gonorrhea, or chlamydia, all of which are sexually transmitted. For other signs of these infections and how to treat them, continue reading.
Yeast (candida, white discharge, thrush)
Yeast is not usually sexually transmitted. It is usually not dangerous, but it can be very uncomfortable. You are more likely to have a yeast infection when you are pregnant, taking antibiotics, or have some other illness like diabetes or HIV infection.
Signs:
- white, lumpy discharge, like milk curd or yogurt, although sometimes there is no abnormal vaginal discharge at all
- red, irritated skin outside and inside your vagina that may bleed
- itchy genitals
- a burning feeling when you pass urine
- a smell like mold or baking bread
Treatment:
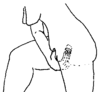
Yeast is treated by putting medicinal creams or inserts in the vagina at night. A health worker can help you know if you have yeast or a different kind of infection. If you are pregnant, it is best to be treated for a yeast infection before giving birth, or the baby can get thrush.
Mild yeast infections will sometimes go away without medicines. Rinsing genitals with or sitting in a pan of warm clean water may reduce itching. If it helps you feel better, do this 2 times a day.
| Medicines for Yeast Infection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Medicine | How much | How to use |
| clotrimazole | one 500 mg insert | put high in the vagina for 1 night only |
| or clotrimazole | two 100 mg inserts | put high in the vagina each night for 3 nights |
| or miconazole | one 200 mg insert | put high in the vagina each night for 3 nights |
| or nystatin | one 100,000 Units insert | put high in the vagina each night for 14 nights |
| Insert these medicines each night, including during your monthly period. Clotrimazole, miconazole, and nystatin inserts may come in other strengths. Follow the instructions to know how many nights to use. They also come as a cream that goes high in the vagina and as creams that can be applied to the skin around the opening to the vagina and inner thighs if these areas are irritated. | ||
Prevention:
Wear loose clothing and underclothes to let air reach the genitals. This helps prevent yeast. Change the underclothes often. Do not put soap in the vagina when bathing. Do not douche.
Bacterial vaginosis, BV
Bacterial vaginosis is not sexually transmitted. However if sex irritates the vagina, it makes getting this infection more likely. If you are pregnant, it can cause your baby to be born too soon.
Signs in the vagina:
- more discharge than usual
- a bad, fishy smell, especially after sex
- mild itching
The antibiotic clindamycin can be used to treat bacterial vaginosis if you know it is not from having sex. If you have these signs and think you may have an STI, then treat for trichomonas at the same time with metronizadole or tinazadole (see below).
| Medicine to treat only Bacterial Vaginosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Medicine | How much | How to use |
| clindamycin | 300 mg | by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days |
| or clindamycin cream | 5 grams of 2% cream (one full applicator) | put high in the vagina at bedtime for 7 days |
| If you have bacterial vaginosis and no other infection, your sexual partners need treatment only if they also have abnormal vaginal discharge | ||
Trichomonas
Trichomonas is an STI caused by a parasite. Trichomonas makes the vagina very uncomfortable and itchy. It also makes getting other STIs, including HIV, more likely. Trichomonas inside the penis often has no signs, but can still pass to a partner during sex without a condom.
Signs in the vagina:
- discharge that is gray, yellow, or green
- bad-smelling discharge
- red and itchy genital area
- pain or burning when you pass urine
If you have any of these signs, or if there is a chance your infection was caused by sex, use one of the medicines in the box below. The medicines for only bacterial vaginosis will not completely treat your infection.
| Medicines to treat Trichomonas or Bacterial Vaginosis or both | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Medicine | How much | How to use | |
| metronidazole | 400 to 500 mg | by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days | |
| or metronidazole | 2 grams (2000 mg) | by mouth, 1 time only | |
| Do not use the single large dose if you are pregnant. | |||
| or tinidazole | 2 grams (2000 mg) | by mouth, 1 time only | |
| or if you are less than 3 months pregnant, | |||
| tinidazole | 500 mg by mouth | 2 times a day for 5 days | |
| Any sexual partners you have need the same treatment as you. | |||
IMPORTANT! Do not drink alcohol during the time you are taking metronidazole or tinidazole. | |||
Gonorrhea and chlamydia
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are serious STIs that can cause infertility, but they are easy to cure if treated early. Often people with gonorrhea or chlamydia have no signs. When there are no signs, tests are needed to know if there is an infection. It is important to test for and treat gonorrhea and chlamydia during pregnancy because these infections can pass to the baby during childbirth. Gonorrhea and chlamydia can have the same signs, so often 2 medicines are given to treat both. A person’s sexual partners will need treatment too.
Itching of the anus or pain passing stool can sometimes be a sign of a STI. If you notice it is slippery when you wipe your bottom, this could be a sign of gonorrhea or chlamydia.
Pain or burning when passing urine can also be from a bladder or kidney infection
Signs in the vagina:
- yellow or green discharge from the vagina or anus
- pain or burning when passing urine
- fever
- pain in the lower belly
- pain or bleeding during sex
Signs in the testicles and penis:
- discharge from the penis
- pain or burning when passing urine
- pain or swelling of the testicles
| Medicines to treat Gonorrhea and Chlamydia | ||
|---|---|---|
| Treatment for abnormal discharge likely to be from STIs | ||
| To stop infection quickly, it is common to give medicines for both gonorrhea and chlamydia at the same time. If there are signs that could be trichomonas, also use a third medicine, metronidazole. | ||
| Where more than 1 medicine is listed, the best choice in each section is shown first. | ||
| Medicine | How much | How to use |
| ceftriaxone | 250 mg | inject into muscle 1 time only |
| In some places, 500 mg may be recommended. | ||
| or cefixime | 400 mg | by mouth 1 time only |
| Only use cefixime if ceftriaxone is not available. | ||
| AND | ||
| azithromycin | 1 gram (1000 mg) | by mouth 1 time only |
| or doxycycline | 100 mg | by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days |
| Do not use doxycycline if you are pregnant and avoid using it if you are breastfeeding. | ||
| or erythromycin | 500 mg | by mouth, 4 times a day for 7 days |