Hesperian Health Guides
Medicines Pages
For example, if you are looking up Hydroxyzine, it comes after Doxycycline but before Metronidazole.
You can also find a medicine in the Medicines Pages by using:
- the problem index. This index lists the health problems discussed in this book and medicines used to treat them. The index gives the page number where information about the health problem can be found. Be sure to read about the problem before treating it with medicine. Remember: good health does not depend only on medicines! The most important “medicine” for good health is good health information.
- the medicine index.This index lists the generic names of medicines and some common brand (commercial) names. If there is a medicine you want to use, you can look it up here to find the number of the page where you can learn more about that medicine.
Both the problem and medicine indexes are arranged in the order of the alphabet.
Contents
- 1 The information about each medicine appears in a box like this:
- 2 acetaminophen or paracetamol (APAP, Panadol, Tempra, Tylenol, others)
- 3 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONacyclovir (Zovirax)
- 4 adrenaline or epinephrine (Adrenalin)
- 5 amoxicillin (Amoxifar, Amoxil, Himox, Megamox, Sumoxil)
- 6 amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Augmentin)
- 7 ampicillin (Amcil, Ampicin, Omnipen, Penbritin, Polycillin)
- 8 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONaspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA, others)
- 9 azithromycin (Zithromax)
- 10 benzathine benzylpenicillin (Bicillin L-A, Penadur L-A, Permapen)
- 11 benzylpenicillin (Celinex, Hi-Do-Pen, penicillin G potassium or sodium)
- 12 Breastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONcefixime (Suprax)
- 13 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONceftriaxone(Nitrocephin, Rocephin)
- 14 cephalexin (Ceporex, Keflex, Keftab)
- 15 activated charcoal (Activated Carbon, Liquid Antidote)
- 16 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women should not take this medicine ciprofloxacin (Ciloxan, Cipro, Ciprobay)
- 17 Breastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONclindamycin (Cleocin, Dalacin)
- 18 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONcodeine
- 19 cotrimoxazole = trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole (AzoGantanol, Bactrim, Coptin, Gantanol, Pologrim, Septra, Sulfatrim, TMP/SMX, Trimpex, others)
- 20 dexamethasone (Decadron, Decilone, Inflam, Maxidex)
- 21 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONdiazepam (Anxionil, Calmpose, Valium)
- 22 dicloxacillin
- 23 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONdiphenhydramine hydrochloride (Bectivo, Benadryl)
- 24 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONdoxycycline (Biocolyn, Doryx, Monodox, Vibramycin, Vibra-Tabs)
- 25 epinephrine or adrenaline (Adrenalin)
- 26 ergometrine maleate, methylergonovine maleate (Anurhage, Ergonovine, Ergotrate, Methergine)
- 27 erythromycin (E.E.S., E-Mycin, Ery-max, Ethril, Ilosone, Ilotycin)
- 28 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women should not take this medicineestrogen (ethinyl estradiol, mestranol)
- 29 ethambutol (Interbutol, Myambutol, Mycrol, Odetol, Triambutol)
- 30 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women should not take this medicinefluconazole (Diflucan)
- 31 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONgentamicin (Bactiderm, Garamycin, Servigenta)
- 32 hepatitis B vaccine (Engerix-B, Recombivax HB)
- 33 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONhydrocortisone or cortisol(Eczacort, Hycotil, Solu-Cortef, others)
- 34 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONhydroxyzine (Atarax, Iterax, Marax, My-Pam, Vistaril)
- 35 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONibuprofen (Actiprofen, Advil, Genpril, Motrin, Nuprin, Rufen, others)
- 36 isoniazid (Bisonid, INH, Isoniazdum, isonicotinic acid hydrazide, Odinah, Zidrid)
- 37 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women should not take this medicineketoconazole (Nizoral)
- 38 magnesium sulfate
- 39 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONmedroxyprogesterone acetate (Amen, Curretab, Cycrin, Depo-Provera, Megestron, Provera)
- 40 methyl ergonovine (Methergine)
- 41 metoclopramide (Plasil, Primperan, Reglan)
- 42 metronidazole (Flagyl, Methoprotostat, Metro, Metroxyn, Satric)
- 43 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONmiconazole (Daktarin, Fungtopic, Micatin, Monistat)
- 44 mifepristone and misoprostol (Mifegyne, Mifeprex) and (Cytotec)
- 45 Pregnant women need to take special careCAUTIONnitrofurantoin (Furadantin, Macrobid, Macrodantin)
- 46 nystatin (Dermodex, Mycostatin, Nilstat, Nystat)
- 47 oxytocin (Oxtimon, Pitocin, Syntocinon, Uteracon)
- 48 paracetamol, acetaminophen (APAP, Panadol, Tempra, Tylenol, others)
- 49 penicillin (Betapen VK, PenVee K, phenoxymethyl penicillin)
- 50 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women should not take this medicinepodofilox (Condylox)
- 51 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONprobenecid (Benemid, Probalan)
- 52 Pregnant women should not take this medicineprogesterone, progestin
- 53 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONpromethazine (Mepergan, Phenergan, Thaprozine)
- 54 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special carepyrazinamide (Isopas, Pyzamed, PZA, Zinamide, Zinastat)
- 55 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONrifampicin, rifampin (Resimin, Rifastat)
- 56 rifapentine (Priftin, Rifapex)
- 57 tetanus toxoid vaccine (Tetavax)
- 58 Pregnant women should not take this medicineBreastfeeding women should not take this medicinetetracycline (Achromycin, Sumycin, Terramycin, Theracine, Unimycin)
- 59 Pregnant women need to take special careBreastfeeding women need to take special careCAUTIONtinidazole (Fasigyn, Simplotan, Tindamax)
- 60 trichloroacetic acid, bichloroacetic acid
- 61 Sources
The information about each medicine appears in a box like this:
acetaminophen or paracetamol (APAP, Panadol, Tempra, Tylenol, others)
Acetaminophen and paracetamol are 2 names for the same drug that is used to ease pain and lower fever. It is one of the safest pain killers. It does not cause stomach irritation and can be used instead of aspirin by people with stomach ulcers. It can also be used during pregnancy.
See paracetamol.
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONacyclovir (Zovirax)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Acyclovir is a medicine that kills viruses and is used to fight herpes, which can cause painful blisters on the genitals, anus, and in the mouth; and shingles, an infection common in people with HIV. Acyclovir does not cure herpes, but it makes sores less painful and keeps them from spreading.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 200, 400 or 800 mg.
Ointment: 5%
- How to use:
- For genital herpes infection or severe oral herpes in a person with HIV: Take 400 mg by mouth 3 times a day, for 7 to 10 days.
For genital and oral herpes sores: Put ointment on sores 5 times a day for 5 to 10 days. Wash hands immediately after touching sores.
For shingles: Take 800 mg by mouth 5 times a day for 7 to 10 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Someone with kidney problems.
- Information you
should know - To shorten the duration and severity of herpes sores, start taking acyclovir as soon as signs start to appear.
- Side effects
- May cause diarrhea, rash, nausea or vomiting.
- Signs of taking too much
- Headache, loss of memory, nausea, cannot pass urine.
adrenaline or epinephrine (Adrenalin)
Adrenaline and epinephrine are two names for the same drug. It is used for severe allergic reaction or allergic shock, for example, allergic reactions to penicillin. It is also used for severe asthma attacks.
See epinephrine.
amoxicillin (Amoxifar, Amoxil, Himox, Megamox, Sumoxil)
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic of the penicillin family used to treat some common infections. Because of high levels of drug resistance, it is used less than it was previously.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 250 and 500 mg
Liquid: 125, 200, 250 or 400 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For common infections: 500 mg to 1 g (1000 mg) by mouth 2 to 3 times a day for 5 to 10 days, depending on location and severity of infection.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use if allergic to medicines of the penicillin family.
- Side effects
- May cause diarrhea, rash, nausea or vomiting. May cause yeast infection in adults or diaper rash in children.
- Information you
should know - If you do not start to get better in 3 days, look for medical help; you may need a different medicine. Take with food.
amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Augmentin)
The combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin improves the ability of amoxicillin to fight drug resistance. This medicine is used to treat womb infections, among others.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 500 mg amoxicillin/ 25 mg clavulanic acid
Liquid: 125 mg amoxicillin + 31.25 mg clavulanic acid in 5 ml; 250 mg amoxicillin + 62.5 mg clavulanic acid in 5 ml.
- How to use:
- For womb infection after birth, when fever has been gone for 48 hours: Give 500 mg amoxicillin + 125 mg clavulanic acid by mouth 3 times a day for 10 days (also use other drugs to treat vaginal discharge).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use if allergic to medicines of the penicillin family.
- Side effects
- Stomach upset, diarrhea, jaundice
- Information you
should know - Take this medicine with food.
- Other medicines
that may work - doxycycline, metronidazole
ampicillin (Amcil, Ampicin, Omnipen, Penbritin, Polycillin)
Ampicillin is an antibiotic of the penicillin family used to treat many kinds of infections. Because of high levels of drug resistance, it is less useful than previously.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets and Capsules: 250 or 500 mg
Liquid: 125 or 250 mg per 5 ml
Powder for mixing injections: 500 mg
- How to use:
- For infection after abortion: Inject 2 grams (2000 mg) into muscle or into vein, then reduce dose to 1 gram (1000 mg) every 6 hours. Also give gentamicin and metronidazole (see drug combinations to treat infection after abortion).
For fever during labor or womb infection after birth: Inject 2 grams (2000 mg) into muscle, then reduce dose to 1 gram (1000 mg) every 6 hours. Also give gentamicin and metronidazole (for drug combinations, see drugs to treat fever during labor and drug combinations to treat womb infection after birth).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use ampicillin if you are allergic to medicines of the penicillin family.
- Side effects
- May cause stomach upset and diarrhea. May cause rash.
- Warning
- If you do not start to get better in 3 days, look for medical help; you may need another medicine.
- Information you
should know - Take this medicine before eating.
- Other medicines
that may work -
for womb infection after birth: see drug combinations for fever during pregnancy.
for infection after abortion: see drug combinations for infection after abortion.
for fever during labor: see drugs combinations for fever during labor.
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONaspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA, others)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Aspirin works against pain, swelling, and fever.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 300, 500 mg and other amounts.
Low dose tablets: 81mg
- How to use:
- For pain, swelling or fever: Take 300 to 600 mg by mouth no more than 6 times a day as needed.
To prevent pre-eclampsia: Take 81 mg by mouth 1 time each day after 12 weeks of pregnancy and until the birth.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Avoid aspirin during the last 3 months of pregnancy except to prevent pre-eclampsia. People with stomach ulcers or bleeding problems should not take aspirin. Do not use before surgery. Do not use if breastfeeding in the first week of the baby’s life. Do not give to children.
- Side effects
- May cause stomach upset, stomach pain, or bleeding problems.
- Information you
should know - Aspirin treats some sicknesses like arthritis and heart problems, but is usually used to ease pain and fever. It is important to find the cause of the pain or fever and cure that. If pain lasts more than 10 days or fever more than 3 days, get medical help.
- Signs of taking too much
- Ringing in the ears, headache, dizziness, confusion, fast breathing.
- Other medicines
that may work - for pain or fever: paracetamol
for pain, fever, or swelling: ibuprofen
for severe pain: codeine
azithromycin (Zithromax)
Azithromycin is an antibiotic of the macrolide family used to treat many STIs. It can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Often comes in:
- Capsules: 250 mg
- How to use:
- For chlamydia or chancroid: Take 1 gram (1000 mg) by mouth 1 time only (also take other drugs for chlamydia or other drugs for chancroid)
For PID: Take 1 gram (1000 mg) by mouth 1 time only. (also take other drugs for PID)
To prevent infection before an abortion: Take 500 mg by mouth 1 time only.
For sudden, severe diarrhea in a pregnant person with HIV: Take 500 mg by mouth 1 time only.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with allergies to erythromycin and other antibiotics of the macrolide family.
- Side effects
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
- Information you
should know - Azithromycin can be taken with or without food.
- Other medicines
that may work
for chlamydia: see drug combinations for chlamydia
for chancroid: see drug combinations for chancroid
for PID: drug combinations for PID
benzathine benzylpenicillin (Bicillin L-A, Penadur L-A, Permapen)
Benzathine penicillin is a long-acting antibiotic of the penicillin family used to treat syphilis, genital ulcers, and other infections, including some sore throats. It is always given as an injection into muscle.
- Often comes in:
- Powder for mixing for injection: 1.2 or 2.4 million Units in a 5 ml vial.
- How to use:
- For syphilis: If the person has had syphilis less than 1 year, inject 2.4 million Units into muscle one time only. If the person has had syphilis for 1 year or more or for an unknown period of time, inject 2.4 million Units into muscle 1 time a week for 3 weeks.
For tetanus in newborns: Inject 100,000 Units into muscle one time only on the way to the ospital.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People who are allergic to medicines of the penicillin family.
- Warning
- Have epinephrine on hand whenever you inject penicillin. Watch for allergic reactions and allergic shock which could start within 30 minutes.
- Other medicines
that may work - for syphilis: doxycycline, erythromycin
to also treat for chancroid
benzylpenicillin (Celinex, Hi-Do-Pen, penicillin G potassium or sodium)
Benzylpenicillin is an antibiotic of the penicillin family used to treat many serious infections.
- Often comes in:
- Powder for mixing for injection: 1 or 5 million Units
- How to use:
- For severe infections: Inject 1 million Units into muscle every 4 hours for 10 to 14 days. For very severe infections, double this dosage.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People allergic to medicines of the penicillin family.
- Warning
- Watch for allergic reactions and signs of shock.
- Other medicines
that may work - ampicillin, ceftriaxone, clindamycin, doxycycline, gentamicin, metronidazole (see medicine combinations for infection after abortion).
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONcefixime (Suprax)
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Cefixime is an antibiotic of the cephalosporin family that is used to treat many infections including gonorrhea and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). However, ceftriaxone is more effective for those infections.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 200 or 400 mg
Liquid: 100 mg in 5 ml
- How to use:
- For gonorrhea, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Take 400 mg by mouth one time only (see how to treat along with chlamydia and drug combinations to treat PID).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use if you are allergic to antibiotics of the cephalosporin family.
- Side effects
- Nausea, diarrhea, headache
- Warning
- Watch for allergic reaction. People who have liver problems should be watched carefully when taking cefixime.
- Other medicines
that may work - for gonorrhea, or for one of the medicines taken in combination for PID: ceftriaxone
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONceftriaxone(Nitrocephin, Rocephin)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Ceftriaxone is a very strong antibiotic of the cephalosporin family that is injected into muscle or vein. It is used for many infections including gonorrhea, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), kidney infections, and serious infection after abortion, childbirth, or miscarriage.
- Often comes in:
- In vials for injection: 250, 500 mg, 1 gram, and 2 grams
- How to use:
- For infection after abortion: Inject 1 to 2 g IM or IV 1 or 2 times a day for 4 to 7 days (see drug combinations to treat infection after abortion).
For PID: Inject 250 mg into muscle one time only. In areas of high resistance, 500 mg may be recommended (see drug combinations to treat PID).
For gonorrhea: Inject 250 mg into muscle one time only. In areas of high resistance, 500 mg may be recommended (see drug combinations to treat STIs).
For kidney infection: Inject 1 gram IM or IV once a day for 10 days.
For chancroid: Inject 250 mg into muscle one time only (see how to treat chancroid and syphilis at the same time).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use if you are allergic to antibiotics of the cephalosporin family, or if you had hives or a severe allergic reaction to penicillin.
- Warning
- Watch for allergic reaction. Always be prepared to treat for allergic reaction and shock when injecting antibiotics.
- Other medicines
that may work - for infection after abortion: see drug combinations to treat.
for PID: see drug combinations to treat.
for kidney infection: ciprofloxacin for chancroid.
cephalexin (Ceporex, Keflex, Keftab)
Cephalexin is an antibiotic of the cephalosporin family used to treat breast infections, bronchitis and some skin infections.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 250 or 500 mg
Liquid: 125 or 250 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For breast or skin infection and infection after female genital cutting: Take 250 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 7 to 14 days. Serious infections may need higher doses, but use no more than 4 g in 24 hours.
For open or infected wounds in people with HIV: Take 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 5 to 7 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not take cephalexin if you are allergic to antibiotics of the cephalosporin family.
- Side effects
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Warning
- Watch for allergic reaction.
- Information you
should know - If you start having bloody diarrhea with fever, stop taking cephalexin and treat with metronidazole.
- Other medicines
that may work - for breast or skin infection: dicloxacillin, erythromycin, penicillin
for infection after female genital cutting: dicloxacillin, erythromycin
activated charcoal (Activated Carbon, Liquid Antidote)
Activated charcoal is a specially prepared charcoal used to treat some poisonings by drugs like aspirin, acetaminophen, phenobarbitol, or other medicines or chemicals, or poisonous mushrooms. After giving activated charcoal, get medical help immediately.
- Often comes in:
- Liquid: 25 g per 120 ml
Powder: 15 g
- How to use:
- Take 30 to 100 g by mouth all at one time and as soon as possible.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not take if you have swallowed lighter fluid, fuel, kerosene or petroleum products.
- Side effects
- Black stools, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Warning
- Get medical help immediately. People who take too much of a drug can get very sick and may need much more help than activated charcoal.
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
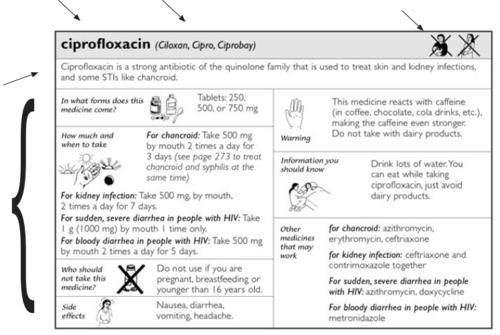
ciprofloxacin (Ciloxan, Cipro, Ciprobay)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
Ciprofloxacin is a strong antibiotic of the quinolone family that is used to treat skin and kidney infections, and some STIs like chancroid.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 250, 500, or 750 mg
- How to use:
- For chancroid: Take 500 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 3 days (see how to treat chancroid and syphilis at the same time).
For kidney infection: Take 500 mg, by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days. Also inject ceftriaxone.
For sudden, severe diarrhea in people with HIV: Take 1 g (1000 mg) by mouth 1 time only.
For bloody diarrhea in people with HIV: Take 500 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 5 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use if you are pregnant, breastfeeding or younger than 16 years old.
- Side effects
- Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache.
- Warning
- This medicine reacts with caffeine (in coffee, chocolate, cola drinks, etc.), making the caffeine even stronger. Do not take with dairy products.
- Information you
should know - Drink lots of water. You can eat while taking ciprofloxacin, just avoid dairy products
- Other medicines
that may work -
for kidney infection: ceftriaxone and cotrimoxazole together.
for sudden, severe diarrhea in people with HIV: azithromycin, doxycycline
for bloody diarrhea in people with HIV: metronidazole
for chancroid: azithromycin, erythromycin, ceftriaxone
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONclindamycin (Cleocin, Dalacin)
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Clindamycin is an antibiotic of the lincosamide family that is used to treat infections of the vagina, pelvis, abdomen, skin, and respiratory tract.
- Often comes in:
- Capsules: 25 mg, 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg
Liquid for injection: 150 mg/ ml
Cream: 2%
- How to use:
- For bacterial vaginosis: Capsules: Take 300 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 7 days. Cream: Put 5 g (one full applicator) of cream high in the vagina each night at bedtime for 7 nights.
For infection after abortion: Inject 900 mg into vein 3 times a day (see drug combinations for post-abortion infections).
For malaria in the first 3 months of pregnancy: Take 300 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 7 days. Also take 600 mg of quinine, 3 times a day for 7 days.
For closed infected wounds in people with HIV: Take 300 to 450 mg by mouth 3 times a day for 7 to 10 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- If you are breastfeeding and this medicine gives your baby diarrhea, stop using it.
- Side effects
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can happen within a few weeks of using this medicine. If it gives you skin rash, stop using it and see a health worker to get a different medicine.
- Warning
- Using for more than 30 days can lead to thrush and yeast infections, and harm people with kidney or liver problems. The vaginal cream can weaken condoms for up to 3 days after use.
- Information you
should know - Using this medicine with erythromycin or chloramphenicol can make both drugs less effective. If you use the cream during your menstrual period, do not use a tampon because it will absorb the medicine.
- Other medicines
that may work - for bacterial vaginosis: metronidazole
for womb infection or infection after abortion: ampicillin, ceftriaxone, doxycycline, erythromycin, gentamicin, metronidazole
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONcodeine
Pregnant women need to take special care
Codeine is a pain killer of the opiate family that also calms coughs and helps you relax and sleep. Only use codeine to calm very bad coughs after you have treated the cause for the cough. Only use codeine for pain when milder pain medicines do not work.
- Often comes in:
- Liquid: 15 mg per ml
Tablets: 15, 30, or 60 mg
Cough syrup: Different strengths
- How to use:
- For coughs: Take 7 to 15 mg 4 times a day, only as needed.
For severe pain: Take 30 to 60 mg 4 to 6 times a day, as needed.
- Side effects
- May cause constipation (difficulty passing stools) and temporary inability to pass urine. Nausea, vomiting, itching, headaches.
- Information you
should know - Codeine is habit forming (addictive). If you use it for several days, you will need more for it to keep working.
- Signs of taking too much
- Sleepiness, stupor, coma.
- Treatment for taking too much
- Inject or use a nasal spray of naloxone (Narcan) for someone who has taken too much codeine. If you do not have it, activated charcoal may help. Seek medical help.
- Other medicines
that may work - for pain: acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen
for severe pain: morphine
for cough: drink plenty of water, use home-made cough syrup
cotrimoxazole = trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole (AzoGantanol, Bactrim, Coptin, Gantanol, Pologrim, Septra, Sulfatrim, TMP/SMX, Trimpex, others)
Cotrimoxazole is a combination of 2 antibiotics (one from the sulfa family) that is used to treat
bladder and kidney infections. It also helps prevent diarrhea, pneumonia, and other infections for
people with HIV.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 120 mg (20 mg trimethoprim + 100 mg sulfamethoxazole), 480 mg (80 mg trimethoprim + 400 mg sulfamethoxazole—called “single strength”), and 960 mg (160 mg trimethoprim + 800 mg sulfamethoxazole—called “double strength”)
Oral suspension: 240 mg (40 mg trimethoprim +
200 mg sulfamethoxazole) per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For bladder infection: Take 960 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 3 days.
For kidney infection: Take 960 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 10 days. Also inject ceftriaxone).
For prevention of diarrhea, pneumonia and other infections for people with HIV: Take 960 mg every day.
For continuous diarrhea in people with HIV: Take 1920 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 14 days. Then take 960 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 21 days (also take other drugs).
For pneumonia for people with HIV: Take 1920 mg by mouth 3 times a day for 21 days.
For closed infected wounds in people with HIV: Take 960 to 1920 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 7 to 10 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- If you are allergic to sulfa antibiotics, do not take this drug.
- Side effects
- Stop taking it if it causes allergic reactions like itching or skin rashes. Also may cause nausea and vomiting.
- Warning
- Take with lots of water.
- Signs of taking too much
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, confusion, sweating
- Other medicines
that may work - for bladder and kidney infection: ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, nitrofurantoin
for continuous diarrhea in people with HIV: metronidazole
dexamethasone (Decadron, Decilone, Inflam, Maxidex)
Dexamethasone is a steroid medicine used to treat allergic shock.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, or 6 mg
Liquid: 0.5 mg per 5 ml, or 1 mg per 1 ml
For injection: 4, 8, 10, 16, or 20 mg per ml
- How to use:
- For allergic shock: Inject 20 mg into muscle. If signs return, take 20 mg by mouth and repeat once if needed.
- Side effects
- If the person has diabetes, it could make it worse for a few hours. Also, it might raise blood pressure.
- Other medicines
that may work - for allergic shock: hydrocortisone
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONdiazepam (Anxionil, Calmpose, Valium)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Diazepam is a tranquilizer used to treat and prevent convulsions and seizures. It also relieves anxiety and helps promote sleep.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 5 or 10 mg
For injections: 5 mg per 1 ml or 10 mg per 2 ml
- How to use:
- For seizures: Put 10 mg of injectable diazepam in the anus using a syringe without a needle. Repeat after 15 minutes if needed, using 10 mg. Use crushed tablets in water if you do not have injectable diazepam.
For alcohol withdrawal: Give 10 mg by mouth. Repeat after 6 hours if needed. If signs continue, give every 6 hours while seeking medical help.
For anxiety or sleeplessness: Take 2.5 to 5 mg by mouth.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should only use diazepam to stop seizures.
- Side effects
- Frequent or large doses of diazepam during pregnancy can cause birth defects.
- Warning
- Diazepam is an addictive (habit-forming) drug. Avoid taking with other drugs that will make you sleepy, especially alcohol.
- Information you
should know - Diazepam does not treat pain. It is very habit-forming.
- Signs of taking too much
- Sleepiness, loss of balance, confusion
- Other medicines
that may work - for seizures: magnesium sulfate
for sleep: diphenhydramine
for anxiety: hydroxyzine
dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is an antibiotic of the penicillin family used to treat breast and skin infections.
- Often comes in:
- Capsules: 125, 250, or 500 mg
Liquid: 62.5 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For breast, skin or other infections: Take 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 7 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not take this drug if you are allergic to penicillin.
- Side effects
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Warning
- Watch for allergic reactions or shock.
- Other medicines
that may work - for breast or skin infections: cephalexin, erythromycin, penicillin
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONdiphenhydramine hydrochloride (Bectivo, Benadryl)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine that dries up mucus in the nose and also makes you sleepy. It is useful for treating itching and sleep problems. It is also a treatment for allergic reactions and allergic shock.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets or capsules: 25 or 50 mg
Syrup: 12.5 mg per 5 ml
Ampules for injection: 10, 30, or 50 mg in 1 ml
- How to use:
- For allergies, mild to moderate allergic reaction, or itching: Take 25 to 50 mg, by mouth, 3 or 4 times a day as needed.
For sleep: Take 25 to 50 mg at bedtime.
For allergic shock: Inject 50 mg into muscle, repeat in 8 hours or sooner if needed.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use for long-term treatment for allergies during pregnancy or breastfeeding. People with asthma should not take it.
- Side effects
- Sleepiness, dry mouth. Sometimes causes nausea and vomiting. In rare cases can have the opposite effect and excite rather than calm you.
- Warning
- Do not use if you need to be alert. Makes the effects of tranquilizers and alcohol dangerously stronger.
- Information you
should know - Only inject diphenhydramine for severe allergic reactions or shock.
- Other medicines
that may work - for allergies: hydroxyzine, promethazine
for sleep: diazepam
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONdoxycycline (Biocolyn, Doryx, Monodox, Vibramycin, Vibra-Tabs)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Doxycycline is an antibiotic of the tetracycline family used to treat many different infections including STIs, pelvic infections, infections after abortions, and others. It is used instead of tetracycline.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 50 mg and 100 mg
- How to use:
- For chlamydia: Take 100 mg, by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days (also take other drugs).
For a person with syphilis less than 1 year: Take 100 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 14 days.
For PID: Take 100 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 14 days (also take other other drugs for PID)
For sudden, severe diarrhea in people with HIV: Take 300 mg by mouth 1 time only.
For closed infected wounds in people with HIV: Take 100 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 7 to 10 days.
For infection prevention after an abortion or deinfibulation: Take 100 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
For infection after an abortion: Take 100 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 10 days (also take other drugs by mouth)
For womb infection after birth, when fever has been gone for 48 hours: Take 100 mg by mouth, 2 times a day for 10 days (also use other drugs).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not take during pregnancy or give to children under 8. Doxycycline can damage a baby’s or child’s teeth and bones. Doxycycline can be taken for a short time during breastfeeding to treat infection, but avoid taking it long-term.
- Side effects
- Diarrhea or upset stomach. Some people get a rash after staying a long time in the sun.
- Warning
- Do not take if pregnant and try to avoid if breastfeeding. Avoid milk, iron pills, and antacids for 2 hours before or after taking.
- Information you
should know - Do not take just before lying down. Sit up while taking pills and drink lots of water to prevent the irritation that swallowing this medicine can cause.
- Other medicines
that may work - for syphilis: benzathine penicillin, erythromycin,
for chlamydia: see medicine combinations to treat along with gonorrhea.
to prevent infection after abortion: erythromycin
for infection after abortion: see drug combinations
for sudden, severe diarrhea in people with HIV: azithromycin, ciprofloxacin
epinephrine or adrenaline (Adrenalin)
Epinephrine and adrenaline are two names for the same drug. It is used for allergic reactions or allergic shock, for example, allergic shock caused by penicillin. It is also used for severe asthma attacks.
- Often comes in:
- Ampules for injection: 1 mg in 1 ml
- How to use:
- For asthma, moderate allergic reaction or allergic shock: Inject ½ mg (½ ml) into the muscle or just under the skin of the upper arm or outer thigh. If needed, give a second dose 5 to 15 minutes after the first, and a third dose 5 to 15 minutes after that (also give other drugs for allergic shock).
- Side effects
- Fear, restlessness, nervousness, tension, headaches, dizziness, increased heart rate.
- Warning
- Be careful never to give more than the recommended amount. Avoid injecting this into the buttocks, instead use the back of the upper arm.
- Information you
should know - Take the person’s pulse before injecting. Do not give more than 3 doses. If the pulse goes up by more than 30 beats per minute after the first injection, do not give another dose.
- Signs of taking too much
- High blood pressure, fast heart beat, stroke.
ergometrine maleate, methylergonovine maleate (Anurhage, Ergonovine, Ergotrate, Methergine)
Ergometrine causes contractions of the womb and its blood vessels and is used to control heavy bleeding after childbirth or an abortion. Ergometrine and methylergonovine are the same drug. After giving this medicine, get help.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: Tablets: 0.2 mg
For injection: 0.2, 0.25 and 0.5 mg in 1 ml vial
- How to use:
- For heavy bleeding after birth: Inject 0.2 mg in the side of the thigh muscle one time. If heavy bleeding has not stopped after 15 minutes, inject another 0.2 mg. Then continue to give every 4 hours as needed. Do not give more than 5 doses (1.0 mg total).
For heavy bleeding due to complications after an abortion: Inject 0.2 mg into muscle, then give 0.2 mg by mouth or injection every 6 hours for 24 hours.
- Side effects
- Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sweating.
- Warning
- Do not use these drugs to start labor or make labor stronger. Never give this medicine before the baby and the placenta have come out.
- Information you
should know - Do not use this drug to cause an abortion because it could kill the pregnant person. (For abortion see Chapter 15).
- Other medicines
that may work - oxytocin, misoprostol
erythromycin (E.E.S., E-Mycin, Ery-max, Ethril, Ilosone, Ilotycin)
Erythromycin is an antibiotic of the macrolide family used to treat many infections, including some STIs, respiratory and skin infections. It can be safely used during pregancy and is widely available.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets or capsules: 200, 250 or 500 mg
Ointment: 1% Powder for solution: 125 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For chlamydia: Take 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 7 days (also take other drugs).
For breast infection, infection after female genital cutting or deinfibulation: Take 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 7 days.
For chancroid: Take 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 7 days (see how to treat chancroid and syphilis at the same time).
For syphilis or PID: Take 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 14 days. For PID, also (see take other drugs).
For newborn eye-care: Use 1% ointment one time only.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use if you are allergic to antibiotics of the macrolide family.
- Side effects
- May upset stomach or cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Information you
should know - Erythromycin works best when taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. If this upsets your stomach too much, take with a little food. Do not break up tablets. Many tablets are coated to prevent strong stomach juices from breaking down the drug before it can begin to work.
- Other medicines
that may work - for breast infection: cephalexin, dicloxacillin
for infection after genital cutting: cephalexin, doxycycline
for STIs: see drug combinations for STIs
for newborn eye-care: povidone-iodine, silver nitrate ointment, tetracycline ointment
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
estrogen (ethinyl estradiol, mestranol)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
Chemical forms of estrogen are used in birth control pills and injections. They are similar to the hormone estrogen made by the ovaries. Estrogen can also be used to treat abnormal bleeding from the womb (uterus). It should no longer be used for problems of menopause (see Chapter 8). For more information, see Chapter 13 and the section on birth control pills, injections, and emergency contraception.
ethambutol (Interbutol, Myambutol, Mycrol, Odetol, Triambutol)
Ethambutol is used to treat tuberculosis (TB) in combination with other drugs. See Chapter 25.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 100 or 400 mg
Syrup: 25 mg/ml
- How to use:
- The doses for tuberculosis medicines differ by region. Do not take more than 1200 mg a day. See a health worker. (Take ethambutol in combination with other drugs.)
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with serious vision problems, including cataracts (cloudy vision), should not take this drug. People with severe kidney problems should talk to a health worker about a modified dosage.
- Side effects
- Ethambutol often causes vision changes in one or both eyes. It might make the area of what you can see smaller, or cause patchy dark spots or “holes”
in your vision. This usually goes away when you stop taking the drug. See a health worker if vision changes do not stop.
- Information you
should know - It is very important that you take the entire course of treatment for tuberculosis, even if it lasts for a year. If not, you might infect other people or get sick again with a kind of TB that is very hard to cure.
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
fluconazole (Diflucan)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
Fluconazole is a strong anti-fungus medicine that is used to treat thrush and other yeast and fungal infections. Use only if you have HIV and other remedies do not work.
- Often comes in:
- Capsule: 50 mg
Liquid: 50 mg per 5 ml
In vials for injection: 2 mg per ml
- How to use:
- For yeast infections of the mouth in people with HIV: Take 100 to 150 mg by mouth each day for 7 to 14 days.
For yeast infections of the throat in people with HIV: Take 100 to 200 mg by mouth each day for 14 to 21 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use during pregnancy or if breastfeeding. Also, anyone who has hepatitis, liver disease, or kidney problems should not take this drug.
- Side effects
- May cause nausea, vomiting.
- Other medicines
that may work - ketoconazole, nystatin
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONgentamicin (Bactiderm, Garamycin, Servigenta)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Gentamicin is a very strong antibiotic of the aminoglycoside family. Use this drug only when someone is vomiting and cannot keep other medicines down or no other antibiotic is available.
- Often comes in:
- In vials for injection: 10 or 40 mg per ml
- How to use:
- For fever during labor or womb infection after birth: Inject 80 mg in the muscle or vein, every 12 hours. Also give ampicillin and metronidazole (see drug combinations to treat womb infection after birth.)
drug combinations to treat fever during labor and to treat fever after birth.
For infection after abortion: Inject 80 mg into muscle or into vein every 8 hours. Also give ampicillin and metronidazole (see drug combinations to treat infection after abortion).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People who are pregnant or who have kidney problems should use this drug very carefully. Do not use this drug if you are allergic to other antibiotics of the aminoglycoside family.
- Side effects
- This drug can damage the kidneys or cause deafness.
- Warning
- Use a different medicine if hearing problems or ringing in the ears start. Give with plenty of fluids.
- Information you
should know - Because of the serious side effects and the difficulty of calculating the dosage, this drug should only be used when safer antibiotics are not available.
- Signs of taking too much
- Ringing in the ears or worsening of hearing. Kidney problems.
- Other medicines
that may work - for fever during labor: see drug combinations.
for womb infection after birth: see drug combinations.
for infection after abortion: ampicillin, ceftriaxone, doxycycline, clindamycin, metronidazole
hepatitis B vaccine (Engerix-B, Recombivax HB)
For hepatitis B vaccination, babies get a series of 3 or 4 injections. The first is given at birth and the others by 6 months of age, either with the DPT series or as part of other vaccinations. Vaccinate older children and adults with the series of 3 injections if they did not receive this vaccination as a baby.
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONhydrocortisone or cortisol(Eczacort, Hycotil, Solu-Cortef, others)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Hydrocortisone is an anti-swelling and anti-itch medicine used to treat rashes. It is also useful for treating hemorrhoids (piles). In its injection form and as tablets it is an important drug for treating allergic shock.
- Often comes in:
- Cream or ointment: in many strengths, often 1%
Tablets: 5, 10, and 20 mg
Liquid for injection and powder for mixing for injection: various strengths
- How to use:
- For rash, itching or piles: Put cream directly on skin 3 or 4 times a day.
For allergic shock: Inject 500 mg into muscle, repeat in 4 hours if needed (also take other drugs for allergic shock). If signs return later, take 500 to 1000 mg by mouth and repeat once if needed.
- Side effects
- Cream may cause thinning and scarring of skin if used for more than 10 days.
- Warning
- Do not use cream with a bandage covering it. Cream can be used safely during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but use tablets with caution.
- Signs of taking too much
- High blood pressure, passing more urine than usual.
- Other medicines
that may work - for allergic shock: dexamethasone,
diphenhydramine
for allergies or itching: diphenhydramine
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONhydroxyzine (Atarax, Iterax, Marax, My-Pam, Vistaril)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine used for allergic reactions, to control itching, and sometimes to treat nausea, vomiting, and anxiety.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 25, 50, or 100 mg
For injection: 25 or 50 mg per 5 ml
Syrup: 10 or 25 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For itching: Take 25 to 50 mg by mouth 3 or 4 times a day.
To relieve anxiety: Take 25 to 50 mg by mouth 4 times a day.
For moderate allergic reactions or hives: Inject into muscle: 25 mg 3 or 4 times a day.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use during first 3 months of pregnancy. In the rest of pregnancy or if breastfeeding, use only if there is no other choice. Do not use this drug if you must stay alert.
- Side effects
- Causes dry mouth, sleepiness, and may cause loss of appetite.
- Signs of taking too much
- Sleepiness
- Other medicines
that may work - for itching, allergy or allergic shock:
diphenhydramine, promethazine
for anxiety: diazepam
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONibuprofen (Actiprofen, Advil, Genpril, Motrin, Nuprin, Rufen, others)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Ibuprofen works against muscle pain, joint pain, swelling, headache, and fever. It is very useful to relieve discomfort during your menstrual period or the flu, and pain from toothache, backache, injury, or arthritis.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 200 mg and larger
Liquid: 100 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- Take 200 to 400 mg 4 to 6 times a day. Do not take more than 2400 mg daily.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with stomach ulcers should not take this drug. Do not use during the last 3 months of pregnancy.
- Side effects
- May cause stomach irritation or pain. Take with food.
- Warning
- Avoid taking within a week of surgery.
- Information you
should know - Causes less irritation if taken with food, especially dairy products, at mealtimes.
- Other medicines
that may work - for pain, swelling and fever: aspirin
for pain and fever: acetaminophen
for severe pain: codeine, morphine
Use in combination with paracetamol for strong pain (see Helping Children Live with HIV.)
isoniazid (Bisonid, INH, Isoniazdum, isonicotinic acid hydrazide, Odinah, Zidrid)
Isoniazid is used to treat tuberculosis (TB) in combination with other medicines. See Chapter 25. People with HIV can use isoniazid, or isoniazid in combination with another TB medicine, to prevent latent TB (TB with no signs) from becoming active TB.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 50, 100, or 300 mg
Syrup: 50 mg per 5ml
- How to use:
- The doses for medicines to treat tuberculosis differ by region. See a health worker. (Take isoniazid in combination with other drugs).
For prevention of TB in adults with HIV: Take 300 mg by mouth every day for 6 to 9 months to 3 years.
Ask if a shorter duration combination treatment is available.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Anyone who has hepatitis, liver disease, or has taken isoniazid before and had liver problems, should not take this drug.
- Side effects
- May cause pain or numbness in arms and legs. Taking 10 mg of vitamin B6 daily can help, especially during pregnancy. Sometimes isoniazid may cause severe hepatitis with signs like tiredness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, or yellowing of eyes. If this happens, stop taking this medicine immediately.
- Information you
should know - Never take more than 300 mg a day if you take it every day, or 900 mg a day if you take it 3 times a week. Take the full course of treatment for tuberculosis. If not, you can infect other people or get sick again with a kind of TB that is very hard to cure.
- Signs of taking too much
- Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, slurred speech, blurred vision, seizures.
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
ketoconazole (Nizoral)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
Ketoconazole is a strong anti-fungus medicine that is used to treat thrush and other yeast infections. Use only if you have HIV and other remedies do not work.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 200 mg
Also comes as 2% skin cream and 1% shampoo
- How to use:
- For yeast infection in the esophagus (the tube from the throat to the stomach) in people with HIV (esophageal thrush): Take 200 to 400 mg by mouth once a day for 14 to 21 days.
- Side effects
- May cause nausea, vomiting.
- Warning
- Do not take if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Do not put cream or shampoo in vagina. Take with food. Do not drink alcohol while using this medicine.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Anyone who has hepatitis or liver disease should not take this drug.
- Information you
should know - This medicine works best if taken with orange juice
- Other medicines
that may work - for yeast infections in the esophagus (the tube from the throat to the stomach) in people with HIV: fluconazole
magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate is the best medicine to treat and prevent seizures in pregnant people with eclampsia.
- Often comes in:
- Injections of 10%, 12.5%, 25%, or 50% solution
- How to use:
- For seizures: Inject 10 g of 50% solution, 5 g into each buttock. Then inject 5 g 50% solution every 4 hours, alternating buttocks. Continue for 24 hours after the baby is born or after the last seizure (whichever is later).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Someone with kidney problems should not be given this drug.
- Warning
- Only use this drug if blood pressure is above 160/110. After giving, continue to check blood pressure. Too much of this medicine can slow down or stop a person’s breathing!
- Information you
should know - Injecting a large amount needs a big needle and may be uncomfortable. You might want to split the dose in half and give 2 smaller shots, one in each hip.
- Signs of taking too much
- Sweating, low blood pressure, weakness, problems breathing.
- Other medicines
that may work - For seizures: diazepam
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONmedroxyprogesterone acetate (Amen, Curretab, Cycrin, Depo-Provera, Megestron, Provera)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is a chemical form of progesterone, a hormone produced naturally by the ovaries. It can be used to prevent pregnancy, and to treat irregular bleeding caused by changing hormones, especially around the time of menopause. For more information, see Chapter 8, “Growing Older,” and Chapter 13, “Family Planning.”
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 2.5, 5, or 10 mg
Liquid for injection: 150 or 400 mg per ml
- How to use:
- For heavy bleeding: Take 10 mg by mouthonce a day for 10 days. If bleeding continues, take for 10 more days
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with hepatitis, or cancer of the breast or cervix should not take this medicine.
- Warning
- If bleeding continues after 20 days of treatment, see a health worker. It could be a serious problem.
methyl ergonovine (Methergine)
Methyl ergonovine causes contractions of the womb and its blood vessels and is used to control heavy bleeding after childbirth. It is the same drug as ergometrine and ergonovine.
metoclopramide (Plasil, Primperan, Reglan)
Metoclopramide is used for digestion system problems, especially nausea and vomiting.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 10 mg
Injection: ampules of 10 mg in 2 ml
- How to use:
- For severe vomiting in people with HIV: Give 10 mg by mouth 3 times a day as needed or inject 10 mg in a vein 3 times a day as needed.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not give this medicine to children under 18 years old. Do not take this if you have high blood pressure, breast cancer, or digestive system problems with bleeding, blockages, or perforations (holes). Use with caution in people over 60 years old, or people with epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, or reduced liver or kidney function.
- Side effects
- Sleepiness or restlessness, dizziness, weakness or involuntary movements of muscles in limbs or face. Side effects increase with the dose and length of time using the medicine.
- Warning
- Do not use if you need to be alert. Do not use with narcotic drugs or alcohol. Stop using if you develop repeated unusual facial movements or body movements or twitches.
- Signs of taking too much
- Sleepiness, slower movements, and confusion, shaking and muscle movement in face or limbs
- Other medicines
that may work - diphenhydramine, promethazine
metronidazole (Flagyl, Methoprotostat, Metro, Metroxyn, Satric)
Metronidazole is used for vaginal infections caused by bacterial vaginosis and trichomonas. It is also effective against some bacteria and amebic dysentery (see Where There Is No Doctor).
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 200, 250, 400, or 500 mg
For injection into vein: 500 mg in 100 ml
- How to use:
- For PID: Take 400 to 500 mg by mouth 3 times a day for 14 days (also take other drugs for PID).
For trichomonas or bacterial vaginosis: Take 400 to 500 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 7 days. If you are not pregnant, you could take instead 2 g (2000 mg) by mouth 1 time only. (if gonorrhea or chlamydia could be present, also give 2 more medicines, see drug combinations for abnormal discharge with an STI.
For infection after abortion: Give 500 mg by mouth 3 times a day or inject 500 mg into a vein 3 times a day (see drug combinations).
For bloody diarrhea in people with HIV: Take 500 mg by mouth 3 times a day for 7 days.
For continuous diarrhea in people with HIV: Take 500 mg by mouth 3 times a day for 7 days (also take other drugs).
For tetanus: Give 500 mg by mouth 3 times a day or inject 500 mg into a vein 3 times a day for 7 to 10 days.
For fever during labor or womb infection after birth: Give 500 mg by mouth every 8 hours. Also give ampicillin and gentamicin (see drug combinations and instructions, for fever during labor and for womb infection after birth).
For womb infection after birth, when fever has been gone for 48 hours: Give 500 mg by mouth 3 times a day for 10 days (also use other drugs).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with liver problems like jaundice (yellow eyes).
- Side effects
- Metallic taste in mouth, dark urine, upset stomach or nausea, headache.
- Warning
- Stop taking it if you have loss of feeling in your hands or feet. In the first 3 months of pregnancy, do not take the one large dose. But if you are breastfeeding, the one large dose is the safest way to take it.
- Information you
should know - Your sexual partner should also be treated. Do not drink alcohol, not even 1 beer, while you are taking metronidazole. It will make you feel very nauseous.
- Other medicines
that may work - for bacterial vaginosis and trichomonas:
tinidazole
for bloody diarrhea in people with HIV: ciprofloxacin
for continuous diarrhea in people with HIV: cotrimoxazole
for fever during labor: see drug combinations.
for womb infection after birth: see drug combinations.
for infection after abortion: see drug combinations.
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONmiconazole (Daktarin, Fungtopic, Micatin, Monistat)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Miconazole is an anti-fungus medicine used to treat vaginal yeast and other fungus infections.
- Often comes in:
- Cream: 2%, 4%
Inserts: 100 mg, 200 mg, and 1200 mg
- How to use:
- For yeast infections:
100 mg inserts: put 1 in the vagina every night for 7 days.
200 mg inserts: put 1 in the vagina every night for 3 days.
For yeast infections of the skin in people with HIV: Put cream on the area 2 times a day for 5 to 7 days.
- Side effects
- Irritation
- Warning
- If miconazole irritates you, stop using it. Avoid having sex for 3-4 days so you do not pass it to your partner. Keep it out of your eyes.
- Other medicines
that may work - for vaginal yeast infections: nystatin, clotrimazole
for yeast infections of the skin: nystatin
mifepristone and misoprostol (Mifegyne, Mifeprex) and (Cytotec)
Mifepristone blocks the effects of progesterone, a hormone that helps the womb maintain a pregnancy. Misoprostol makes the womb contract and expel a pregnancy. When taken together, these medicines are very safe and effective in ending a pregnancy, especially if they are taken early in a pregnancy. Misoprostol can also be used by itself, but is more effective when both medicines are used together.
Misoprostol can also be used to stop bleeding after birth or incomplete abortion, or if the placenta takes more than 1 hour to come out. It is also used for stomach ulcers.
Before using these medicines, read Chapter 15, “Abortion.”
- Often comes in:
- mifepristone: Tablets, 200 mg
misoprostol: Tablets, 100 or 200 mcg
- How to use:
- To end a pregnancy with both mifepristone and misoprostal: For a pregnancy of less than 12 weeks, swallow 200 mg mifepristone. After 1 to 2 days, dissolve 800 micrograms misoprostol in the vagina or in the mouth (between gums and cheeks or under the tongue for about 30 minutes, then swallow what is left). Repeat this dose of 800 mcg misoprostol every 3 hours until the abortion has completed. For a pregnancy of 12 weeks or more, swallow 200 mg mifepristone and after 1 to 2 days, use 400 micrograms of misoprostol every 3 hours until the abortion is complete. The womb is more sensitive to misoprostol in later weeks, so use this lower dose for later pregnancies.
To end a pregnancy with misoprostol by itself: For a pregnancy of less than 12 weeks, dissolve 800 micrograms misoprostol in the vagina or in the mouth (between gums and cheeks or under the tongue for about 30 minutes, then swallow what is left). Repeat this dose of 800 mcg misoprostol every 3 hours until the abortion has completed. For a pregnancy of more than 12 weeks, use 400 micrograms misoprostol every 3 hours until the abortion is complete. The womb is more sensitive to misoprostol in later weeks, so use this lower dose for later pregnancies.
For heavy bleeding after birth or abortion: Dissolve 800 micrograms misoprostol in the mouth under the tongue for about 30 minutes, then swallow what is left. If the person cannot swallow, put pills in the rectum. Wear a glove while pushing in the pills.
- Side effects
- You may have nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, and slight fever in the first few hours after taking misoprostol. These signs will go away on their own.
- Warning
- Never use misoprostol to speed up or start a labor. It could cause the womb to tear open.
When using these medicines to end a pregnancy, be ready to get medical help if the womb does not empty completely or if very heavy bleeding continues after the abortion is complete.
The womb is more sensitive to misoprostol in later weeks of pregnancy, so a lower dose is used for later pregnancies. A higher dose can harm the womb.
Where abortion is restricted, serious legal trouble can result if someone suspects a person tried to have an abortion. Because misoprostol usually does not dissolve completely in the vagina, if there is a problem with the abortion and medical help is necessary, undissolved pieces of pills might be found there. Taking misoprostol between the cheeks and gums or under the tongue is safer where abortion is not completely legal.
- Information you
should know - Taking misoprostol, with or without mifepristone, is more effective the earlier it is taken in pregnancy. When taken later in pregnancy there are more side effects, like heavier vaginal bleeding.
For what to expect when using these medicines for abortion, see Safe Methods of Abortion
Pregnant women need to take special care
CAUTIONnitrofurantoin (Furadantin, Macrobid, Macrodantin)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Nitrofurantoin is an antibiotic used to treat kidney and bladder infections.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 25, 50 or 100 mg
Suspension: 25 mg/5 ml
- How to use:
- For bladder infections: Take 100 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Someone whose kidneys did not work well before they got an infection should not use this drug. Do not use this drug in the last month of pregnancy
- Side effects
- Nausea or vomiting, headaches, passing gas. To limit these, take with milk or food.
- Information you
should know - If you do not feel better in 2 days (48 hours), the infection may be resistant to this medicine. If possible, check with a health worker or take other medicines.
- Signs of taking too much
- Vomiting, chest pains. Urine may turn dark yellow or brown.
- Other medicines
that may work - for bladder infections: cotrimoxazole
nystatin (Dermodex, Mycostatin, Nilstat, Nystat)
Nystatin is an anti-fungus medicine used to treat yeast infections in the mouth (thrush), the vagina,
or the skin.
- Often comes in:
- Vaginal inserts: 100,000 U
Lozenges for the mouth: 200,000 U
Tablets: 500,000 U
Cream: 100,000 U per gram
Liquid: 100,000 U per ml
- How to use:
- For yeast infections of the mouth in people with HIV: Put 1 ml of liquid (100,000 U) in mouth, hold for 2 minutes, then swallow. Do this 4 times a day for 7 days. Or suck one 500,000 U tablet 4 times a day. Keep using for at least 2 days after signs of infection go away.
For yeast infections of the skin in people with HIV: Keep area dry and put cream on the area 2 times a day for 5 to 7 days.
For vaginal yeast infections: Put a 100,000 U insert or 1 gram of cream high in the vagina each night for 14 nights.
- Warning
- If nystatin causes you irritation, stop using it. Avoid having sex for 3-4 days so you do not pass the infection to your partner
- Information you
should know - Nystatin works only against candida yeast infections, while clotrimazole and miconazole work against other fungal infections as well. Clotrimazole may be less costly and easier to use.
- Other medicines
that may work - for yeast infections: miconazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole
oxytocin (Oxtimon, Pitocin, Syntocinon, Uteracon)
Oxytocin is used to cause contractions of the womb and its blood vessels to control heavy bleeding after childbirth or if the placenta takes more than 1 hour to come out.
- Often comes in:
- For injection: 10 Units in 1 ml
- How to use:
- For heavy bleeding after birth: Inject 10 units in the side of the thigh muscle one time. If heavy bleeding has not stopped after 30 minutes, give another medicine for postpartum hemorrhage (see other medicines).
- Side effects
- Oxytocin can cause the womb to contract so strongly that it will not relax after and may even tear the womb. Also, oxytocin can cause high blood pressure.
- Warning
- Do not use this drug to cause an abortion, because it could kill the pregnant person. (See Chapter 15, “Abortion.”)
Do not use oxytocin to speed up or strengthen labor. This can be dangerous to both the person giving birth and the baby. Do not give it before the baby is out.
- Other medicines
that may work - for heavy bleeding after birth: ergometrine, misoprostol
paracetamol, acetaminophen (APAP, Panadol, Tempra, Tylenol, others)
Paracetamol and acetaminophen are 2 names for the same drug, which is used to ease pain and lower fever. It is one of the safest pain killers. It does not cause stomach irritation, so it can be used instead of aspirin or ibuprofen by people with stomach ulcers. It can also be used during pregnancy, and is safe at lower doses for children.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 100, 325 and 500 mg
Liquid: 120 or 160 mg per 5 ml
Inserts: 80, 120, 300, 325, or 650 mg
Drops: 80 mg per 0.8 ml
- How to use:
- Take 500 to 1000 mg, by mouth, 4 to 6 times a day as needed, but do not take more than 4,000 mg a day.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not take acetaminophen if you have liver or kidney damage.
- Warning
- If your fever or pain lasts for more than 3 days, get medical help. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if you take too much or if taken regularly with or after drinking alcohol. Taking more than 4000 mg in a day can be very dangerous.
- Information you
should know - Acetominophen does not cure the sickness, it only eases the pain or the fever. It is important to find the cause of the pain or fever and cure that.
- Signs of taking too much
- Nausea
Vomiting
Pain in the stomach
penicillin (Betapen VK, PenVee K, phenoxymethyl penicillin)
Penicillin is an antibiotic used to treat mouth, tooth, skin, and many other infections.
Unfortunately a lot of resistance to penicillin has developed and it is less useful than previously.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 250, 500 mg
Liquid: 125 or 250 mg per 5 ml
- How to use:
- For mild and moderate infections: Take 250 to 500 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 10 days. For more serious infections, take 500 to 1000 mg by mouth 4 times a day for 10 days.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not take if you are allergic to any antibiotics of the penicillin family.
- Side effects
- Rash
- Warning
- Watch for allergic reactions and allergic shock.
- Other medicines
that may work - dicloxacillin, erythromycin
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
podofilox (Condylox)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
Podofilox is a liquid or gel that can be put directly on genital warts to shrink them. Do not confuse it with podophyllin, also used for genital warts, but more harmful if not used correctly. Podofilox is safer to use.
- Often comes in:
- Liquid: 0.5%
Gel: 0.5%
- How to use:
- Put liquid on warts with a cotton swab or clean cloth rolled to a fine point. The gel can be put on with a finger. Use 2 times a day for 3 days, then stop using for 4 days. Repeat the 3 days of treatment and 4 days without treatment for up to 4 weeks total. Stop when the warts are gone.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use this if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Side effects
- Podofilox can irritate skin, causing it to thin, break, and bleed.
- Warning
- If there is bleeding, swelling, or severe pain, wash it off with soap and water and do not use it again.
- Information you
should know - Do not have sex on the days you use podofilox. If the warts remain after 4 weeks, do not keep using podofilix. See a health worker to get a different treatment.
- Signs of taking too much
- Nausea, vomiting, trouble breathing, seizures, coma. These signs can be caused by putting too much medicine on the skin.
- Other medicines
that may work - for genital warts: trichloracetic acid, bichloracetic acid
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONprobenecid (Benemid, Probalan)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Used with some antibiotics of the penicillin family, probenecid increases the amount of penicillin in the blood and makes it last longer, increasing the effectiveness of treatment.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 500 mg
- How to use:
- Take 500 mg to 1 gram (1000 mg) by mouth each time you use an antibiotic from the penicillin family.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not give probenecid to children under 2 years old.
- Side effects
- It sometimes causes headache, nausea, or vomiting.
- Warning
- Use with caution during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and if you have a stomach ulcer.
- Signs of taking too much
- Vomiting
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
progesterone, progestin
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Progestin is a chemical found in birth control pills and injections, which is similar to the hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries. It is also used to treat irregular bleeding caused by changing levels of hormones. For more information, see the sections on family planning (Chapter 13 and Oral Contraceptives).
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONpromethazine (Mepergan, Phenergan, Thaprozine)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Promethazine is an antihistamine that dries up mucus and makes you drowsy. It is used for allergic reactions, to sleep at night, and to help stop uncontrollable vomiting
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 10, 12.5, 25, or 50 mg
Syrup: 5 mg per 5 ml
Injection: ampules of 25 or 50 mg in 1 ml
Rectal inserts: 12.5, 25, or 50 mg
- How to use:
- For moderate allergic reaction: Give 25 mg by mouth or injection into muscle. Repeat in 8 hours or sooner if needed.
For allergic shock: Inject 50 mg into muscle. Repeat in 8 hours or sooner if needed. (See information on treating allergic reactions and shock.)
For sleep: Take 25 to 50 mg at bedtime.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women should not use this drug regularly. Do not take this if you need to stay alert. Do not give to children under 2 years.
- Side effects
- Often causes dry mouth and blurry vision. Sometimes causes twitching in body, face and especially eyes and neck.
- Warning
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women should take with caution. Do not drive or use heavy machines if you are taking this medicine.
- Signs of taking too much
- Unconsciousness, seizures.
- Other medicines
that may work - for allergy or allergic reaction: diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
pyrazinamide (Isopas, Pyzamed, PZA, Zinamide, Zinastat)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Pyrazinamide is used to treat tuberculosis (TB) (see Chapter 25).
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 150, 400, or 500 mg
Liquid: 30 mg/ml
- How to use:
- The doses for tuberculosis medicines differ from region to region. See a health worker. (Take pyrazinamide in combination with other drugs for TB).
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with liver damage or hepatitis should not take this medicine.
- Side effects
- Yellow skin or eyes, fever, loss of appetite, tiredness, liver tenderness, gout or arthritis. If you have any of these problems, get medical help.
- Warning
- Anyone who is pregnant or breastfeeding should use this drug with caution since its effects on the baby are not known. Take the entire course of treatment for tuberculosis. If not, you might infect other people or get sick again with a kind of TB that is very hard to cure.
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONrifampicin, rifampin (Resimin, Rifastat)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Rifampicin is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis (TB) (see Chapter 25) and other kinds of infections, including leprosy (Hansen’s Disease). Rifampicin is similar to but not the same as rifapentine. You will never use the two together.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 150 or 300 mg
Liquid: 25 mg/ml and 50 mg per 5 ml
Ampules for injection: 600 mg
- How to use:
- Doses for tuberculosis medicines differ from region to region. See a health worker. (Take rifampicin in combination with other drugs for TB). Do not take more than 600 mg a day.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People with liver damage or liver disease should avoid this medicine.
- Side effects
-
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, cramps
- Hot face, itching, rash
- Headaches, fever, chills, bone pain
- Yellow skin or eyes
Except for yellow skin or eyes, these usually happen 2 to 3 hours after taking this medicine and can sometimes be avoided by taking the medicine with food
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, cramps
- Information you
should know - May turn urine, stool, tears, sweat, or spit a red-orange. It will stain contact lenses too. Reduces the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. Take the entire course of TB treatment to prevent drug resistance and infecting others.
rifapentine (Priftin, Rifapex)
Rifapentine is an antibiotic used to treat and prevent tuberculosis (TB) (see Chapter 25). Rifapentine is similar to but not the same as rifampicin. You will never use the two together.
- Often comes in:
- Tablet: 150 mg
- How to use:
- Doses for tuberculosis medicines differ by region. See a health worker. (Take rifapentine in combination with othe drugs.)
For prevention of TB in adults with HIV: Ask if a combination treatment is needed. (See isoniazid.)
- Who should not take this medicine?
- People who have jaundice (yellow skin or eyes) or liver disease should not take this medicine. People who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take rifapentine.
- Side effects
- May turn urine, stool, tears, sweat, or spit red-orange. Makes hormonal contraceptives less effective.
- Information you
should know - Complete the full course of TB treatment to prevent drug resistance and infecting others. See a health worker and get tested for drug resistance if signs do not improve after first 2 months of treatment.
tetanus toxoid vaccine (Tetavax)
Tetanus toxoid vaccine is an immunization that prevents tetanus infection. It can be given during or after pregnancy, or after an abortion. 2 injections (or better still, 3 injections) are given during pregnancy, and will also prevent this deadly infection in the newborn baby.
- Often comes in:
- Liquid for injection: 4, 5, or 10 U per 0.5 ml
- How to use:
- To be safe from tetanus for your entire life, you must get 5 immunization injections, and then one injection every 10 years. For each immunization: Give 1 injection of 0.5 ml into the muscle of the upper arm.
- Side effects
- Pain, redness, warmth, slight swelling.
- Information you
should know
Tetanus immunizations should be given to everyone, starting in childhood. Tetanus immunization is often given to children as part of a combined immunization called DPT, and the three DPT immunizations are equal to the first 2 tetanus toxoid immunizations. Teens and adults may get the combined Td immunization. Every country has its own schedule. The example below shows the minimum time in between injections for adults in one schedule.
First.......................As soon as possible
Second..................4 weeks after the first
Third.................6 months after the second
Fourth...................1 year after the third
Fifth...................1 year after the fourth
Booster.....Every 10 years after last injection
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
tetracycline (Achromycin, Sumycin, Terramycin, Theracine, Unimycin)
Pregnant women should not take this medicine
Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine
Tetracycline is an antibiotic of the tetracycline family. It is used to treat many infections including respiratory infections, diarrhea, and other infections. Doxycycline works for all the same infections, may cost less and is easier to take.
- Often comes in:
- Capsules: 100, 250, or 500 mg
Ointment: 1%
- How to use:
- For baby eye care: Put a bit of ointment in each eye at birth, one time only. See information about care of the eyes.
- Who should not take this medicine?
- Do not use tetracycline if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Do not give to children under 9 years old except for baby eye-care. Do not take if allergic to antibiotics of the tetracycline family.
- Warning
- Do not take within 1 hour of eating dairy products or antacids. Do not take if past expiration date.
- Information you
should know - Tetracycline does no good in fighting common colds or preventing STIs.
- Side effects
- If you spend a lot of time in the sun it can cause skin rashes. It may cause diarrhea or upset stomach.
- Other medicines
that may work - for newborn eye care: erythromycin ointment
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
CAUTIONtinidazole (Fasigyn, Simplotan, Tindamax)
Pregnant women need to take special care
Breastfeeding women need to take special care
Tinidazole is used for vaginal infections caused by trichomonas. It is also effective against some amoebas, parasites, and giardia. It is similar to metronidazole but you don’t have to take it as long.
- Often comes in:
- Tablets: 250 mg, 500 mg
- How to use:
- For trichomonas or bacterial vaginosis: Take 2 grams (2000 mg) by mouth one time only, but not if pregnant. If less than 3 months pregnant: Take 500 mg by mouth 2 times a day for 5 days.
- Side effects
- Metallic taste in mouth, upset stomach or nausea, headache.
- Warning
- Your sexual partner should also be treated. Do not drink alcohol, not even one beer, while you are taking tinidazole or for 3 days after. It will make you feel very nauseous. Avoid this medicine if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Information you
should know - Drink a glass of water after taking this medicine.
- Other medicines
that may work - for trichomonas or bacterial vaginosis: metronidazole
trichloroacetic acid, bichloroacetic acid
Trichloroacetic acid or bichloroacetic acid are applied directly to genital warts to shrink them. To avoid serious burns, ask an experienced health worker to do this.
- Often comes in:
- Liquids in strengths between 10% and 35%
- How to use:
- Put on wart once a week for 1 to 3 weeks, as needed. If there is too much pain, wait longer before the next treatment.
- Warning
- Use very carefully. It can burn normal skin badly enough to cause a scar.
- Information you
should know - First protect the area around the wart with petroleum gel. Use a swab or clean cloth rolled to a fine point to slowly apply small amounts directly to warts until they turn white. It will hurt for 15 to 30 minutes. If it touches healthy skin, wash it off right away with soap and water.
- Other medicines
that may work - for genital warts: podofilox
Sources
- Centers for Disease Control (2020) Update to CDC's Treatment Guidelines for Gonococcal Infection, 2020
- Cleveland Clinic (2022) Podofilox topical solution
- Drugs.com (2022) Metoclopramide Side Effects
- Drugs.com (2021) Podofilox topical
- Médecins Sans Frontières (2021) Clinical guidelines - Diagnosis and treatment manual
- Médecins Sans Frontières (2021) Essential drugs
- Médecins Sans Frontières (2019) Essential obstetric and newborn care
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2021) British National Formulary 81
- UpToDate (2022) Acyclovir (systemic): Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Amoxicillin: Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Cefixime: Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Cephalexin: Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Ciprofloxacin (systemic): Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) First-trimester pregnancy termination: Medication abortion
- UpToDate (2022) Metoclopramide: Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Metronidazole (systemic): Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Penicillin G (intravenous and short-acting intramuscular): Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Penicillin V potassium (oral): Drug information
- UpToDate (2022) Postpartum hemorrhage: Medical and minimally invasive management
- UpToDate (2021) Treatment and prevention of Pneumocystis infection in patients with HIV
- UpToDate (2022) Tuberculosis in Pregnancy
- World Health Organization (2022) Abortion care guideline
- World Health Organization (2021) Guidelines for the management of symptomatic sexually transmitted infections
- World Health Organization (2017) Managing complications in pregnancy and childbirth
- World Health Organization (2021) Model List of Essential Medicines - 22nd list, 2021
- World Health Organization (2015) Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and newborn care: A guide for essential practice (3rd edition)
- World Health Organization (2021) SEARO IMAI district clinician manual: hospital care for adolescents and adults: guidelines for the management of illnesses with limited-resources
- World Health Organization (2021) SEARO IMAI district clinician manual: hospital care for adolescents and adults: guidelines for the management of common illnesses and notifiable diseases
- World Health Organization (2022) World Health Organization consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment - drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, 2022 update
- World Health Organization (2016) World Health Organization guidelines for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- World Health Organization (2016) World Health Organization guidelines for the treatment of Treponema pallidum (syphilis)


