Hesperian Health Guides
Treating Burns
HealthWiki > A Community Guide to Environmental Health > Appendix A: Safety and Emergencies > Treating Burns
 |
For any burn:
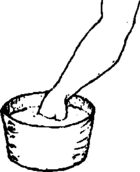
- Stop the burning by putting the burned part in cool water at once. Continue to cool the burn for at least 20 minutes.
- Relieve pain with aspirin or other pain medicine.
- Prevent shock.
For minor burns, no other treatment is needed.
For chemical burns, radiation burns, electrical burns, and burns that cause blisters (2nd degree burns):
Then take the person to a health worker or hospital as soon as possible.
Take the person to a hospital if you think they have burned their airway. Signs include:
- burns around the mouth or nose, or burns inside the mouth.
- mental confusion, unconsciousness, or coughing a lot from inhaling smoke.
Also, take a person to the hospital who has serious burns on the face, eyes, hands, feet, or genitals.
Any person who is been badly burned can easily go into shock because of combined pain, fear, and the loss of body fluids from the oozing burn. Comfort and reassure the person, ease pain, treat shock, and give plenty of liquids.


