Hesperian Health Guides
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that can result from a large burn, losing a lot of blood, severe illness, dehydration, severe allergic reaction, acute toxic exposure, or other emergency situation.
Signs of shock
- Mental confusion, weakness, dizziness, or loss of consciousness
- Weak, rapid pulse
- Cold sweat: pale, cold, damp skin
- Blood pressure drops dangerously low
To prevent or treat shock
At first sign of shock, or if there is risk of shock:

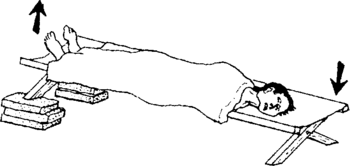
- Have the person lie down with his feet a little higher than his head.
- Stop any bleeding and treat any wounds.
- If the person feels cold cover him with a blanket.
- If the person is able to drink, give sips of water. If he is dehydrated, give a lot of liquid, and rehydration drink.
- If the person is in pain, give aspirin or other pain medicine, but not one with a sedative, such as codeine.
- Stay calm and reassure the person.
If the person is unconscious:
- Lay him on his side with his head low, tilted back and to the side (see above). If he has a neck or spine injury, do not tilt his head or move his back.
- If he has vomited, clear his mouth right away.
- Do not give anything by mouth until he becomes conscious.
- Seek medical help.
This page was updated:05 Jan 2024


