Hesperian Health Guides
7 signs of illness in children
HealthWiki > Helping Children Live with HIV > Chapter 12: Common health problems > 7 signs of illness in children
By understanding what 7 main signs of illness mean, you may be able to find the cause of the problem and act on it.
- Diarrhea, dehydration, and vomiting
- Difficulty breathing and cough
- Fever and seizures
- Sore throat, mouth sores, and thrush
- Skin problems
- Pain, discomfort, and lack of energy
- Low weight, slow growth, and malnutrition

If a child with HIV has any of these problems, she needs your care and attention. If any one problem is severe, or if she has 2 or 3 problems, she needs medical help. The “Quick reference for health problems” on the next two pages can tell you where to find out more.
If it is not difficult you to go to a clinic or hospital, it may be best to take a child with HIV for medical help whenever he is ill. Talk to the health workers about the signs of illness you see in your child, when to come in, and when to manage care at home.
Until you can get to a clinic or hospital, or even if you cannot go at all, there are still things you can do to help your child. This chapter can help you treat some illnesses, and so can your family, friends, and neighbors. Reach out for support, particularly to other people who have experience with children who have HIV.

Contents
Quick reference for health problems
Diarrhea, dehydration, and vomiting
Diarrhea is more serious when a child has other signs.
| Diarrhea with dehydration |
|
Diarrhea, dehydration, and vomiting. |
| Diarrhea with blood or pus in stool, but no fever |
|
Dysentery. |
| Diarrhea with blood or pus in stool, with fever |
|
Shigella and other bacterial infections. |
| Diarrhea is yellow and bubbly |
|
Giardia. |
| Diarrhea with vomiting |
|
Virus or unclean water. |
| Diarrhea with vomiting and fever |
|
Virus or cholera. |
| Boiling water makes it safe to drink and prevents diarrhea. | 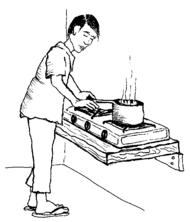 |
Difficulty breathing and cough
Breathing problems are more serious when the child also has other signs:
| Breathing problems and fever |
|
Pneumonia, or colds and flu. |
| Cough with fever for more than 1 week |
|
Tuberculosis (TB). |

Fever and seizures
A high fever is a more serious when the child also has other signs.
| High fever with seizures or convulsions |
|
Seizures and convulsions. | |
| High fever with rash | Dengue or measles . | ||
| High fever with fast breathing, difficulty breathing, or cough |
|
 |
Pneumonia, or bacterial infection or sepsis, or meningitis. |
| High fever with chills or sweats |
|
Malaria, or dengue. | |
| High fever with bad headache, stiff neck |
|
Meningitis. | |



