Hesperian Health Guides
Dengue Fever (Breakbone Fever)
HealthWiki > A Community Guide to Environmental Health > Chapter 8: Health Problems from Mosquitoes > Dengue Fever (Breakbone Fever)
Dengue fever is caused by a virus spread by a black mosquito with bands of white dots that look like white stripes from a distance. Their legs are also striped. This mosquito is sometimes called the "yellow fever mosquito" because it can also carry yellow fever. Dengue usually occurs during the hot, rainy season. It is most common in cities, in places where water collects, and where there is poor drainage.
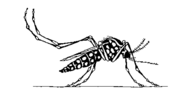
The first time a person gets dengue, she can usually recover with rest and lots of liquids. But when a person gets it a second time or any time after that, it can be much more dangerous and may even cause death.
Signs
When first sick, a person gets a sudden high fever with chills, severe body aches (dengue is sometimes called "bone-break" or "breakbone" fever), a headache, and sore throat. The person feels very ill and weak. After 3 to 4 days, the person usually feels better for a few hours to 2 days. Then illness returns for 1 or 2 more days, often with a rash that begins on the hands and feet. The rash spreads to the arms, legs, and body (but usually not the face).
Babies, young children, and older people, or people with weak immune systems (such as people with HIV), are especially at risk for a more severe form of dengue called hemorrhagic dengue. If not treated right away, this form of dengue causes bleeding from the skin and can lead to death.
Treatment
There is no medicine to treat dengue, and no vaccine to prevent it. It most cases, dengue can be treated at home with bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking ibuprofen or paracetamol (not aspirin) to reduce pain and fever.
Prevention
The mosquito that spreads dengue breeds in clean standing water. Unlike the malaria mosquito, the dengue mosquito bites mostly during the day. For this reason, bed nets have little effect except for small children or older people who sleep during the day. Dengue mosquitoes usually stay in shady, dark places, such as under tables or beds, or in dark corners.
To prevent dengue, avoid mosquito bites and practice community mosquito control.


