Hesperian Health Guides
Abnormal discharge from the vagina
HealthWiki > A Book for Midwives > Chapter 18: Sexually transmitted infections > Abnormal discharge from the vagina

Most women have some discharge (wetness) from the vagina. This discharge is the way the vagina cleans itself. The discharge changes during the days of the monthly cycle and also during pregnancy.
But a major change in the amount, color, or smell of the vaginal discharge can mean there is an infection of the genitals. The infection could be an STI—such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomonas—or might be a vaginal infection that does not spread sexually, such as PID, yeast, or BV.
Contents
Chlamydia and gonorrhea
Chlamydia and gonorrhea are serious STIs that are easy to cure if treated early. If they are not treated, they can lead to severe infection or infertility, and chlamydia can lead to tubal pregnancy. Many people with chlamydia or gonorrhea have no signs. And someone who is infected can pass chlamydia or gonorrhea to a sexual partner with or without showing signs.
It is especially important to test for and treat chlamydia and gonorrhea during pregnancy because these infections can pass to the baby during birth. If someone who is pregnant cannot be tested but she or her partner have signs, they should both be treated, to be safe.
Signs in a woman

- change in vaginal discharge
- bleeding between menstrual periods or after sex
- pain when urinating or during sex
- pain, bleeding, or discharge from the anus
- or no signs at all
Signs in a man

- discharge from the penis
- pain or burning while urinating
- pain or swelling in the testicles (balls)
- or no signs at all
Treatment
It is very common to have chlamydia and gonorrhea at the same time. If you are not sure whether the woman has chlamydia or gonorrhea or both, treat her and her partner for both infections.
Note: In the past, penicillin was used to cure gonorrhea. In many places, penicillin no longer kills gonorrhea because of drug resistance. Find out which drugs work best in your area.
| To treat chlamydia |  |
||||
|
by mouth, 1 time only | ||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days | ||||
| Do not give doxycycline to people who are pregnant and avoid using with people who are breastfeeding. | |||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 4 times a day for 7 days | ||||
| To treat gonorrhea | |||||
|
in the muscle, 1 time only | ||||
| In some places, 500 mg may be recommended. | |||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth,1 time only | ||||
Chlamydia and gonorrhea can infect babies

A woman with chlamydia or gonorrhea can pass these infections to a baby during birth (many women have no signs). This can cause eye infection and blindness in the baby, or serious lung problems. A chlamydia or gonorrhea infection in the eyes usually causes a thick yellow discharge from the eyes within the first month.
| To treat chlamydia or gonorrhea or both: |  |
||||
| If the baby is less than 7 days old | |||||
|
in the thigh muscle, 1 time only | ||||
| If the baby is 7 to 28 days old | |||||
|
in the thigh muscle, 1 time only | ||||
| and | |||||
|
by mouth, 1 time a day, for 3 days | ||||
| OR | |||||
|
in the thigh muscle, 1 time only | ||||
| and | |||||
|
by mouth, 4 times a day, for 14 days | ||||
To prevent eye infection in babies, put antibiotic ointment into every baby's eyes soon after birth.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
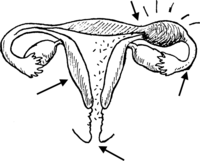
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious infection of the womb, tubes, or ovaries. PID is most often caused by an STI infection that is not treated or not completely treated — usually gonorrhea, chlamydia, or both. PID can also be caused by other infections that are not sexually transmitted, like bacterial vaginosis.
When PID is not treated, it can cause long-term pain, serious illness, scarring or infected growths (abscesses) in the womb and tubes, and death. Women who have (or had) PID are more likely to have a tubal pregnancy or difficulty getting pregnant.
Signs of PID
- pain in the lower belly that can be mild or severe
- fever over 38°C (100.4°F)
- feeling very ill and weak
- unusual bleeding or bad-smelling discharge from the vagina
- pain or bleeding during sex
| To treat PID |  |
||||
| This infection is usually caused by several germs, so 3 medicines are used together. Give 1 medicine from each of the first 2 sections below and also give metronidazole. | |||||
|
by mouth, 2 times a day for 14 days | ||||
| Do not give doxycycline to people who are pregnant and avoid using with people who are breastfeeding. | |||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 1 time only | ||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 4 times a day for 14 days | ||||
| AND | |||||
|
in the muscle, 1 time only | ||||
| In some places, 500 mg may be recommended. | |||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 1 time only | ||||
| AND | |||||
|
by mouth, 3 times a day for 14 days | ||||
| Do not drink alcohol during the time you are taking metronidazole. | |||||
| If the woman is not better after 2 days and 2 nights (48 hours), or if she has high fever or vomiting, she should go to a medical center right away. She needs strong IV medicines (in the vein). | |||||
Trichomonas (trich)
Trichomonas infection can be very uncomfortable, but is not dangerous itself. If untreated, it can make it easier to get other STIs including HIV, can make getting pregnant more difficult, and can make certain types of cancer more likely. In pregnant women, it can cause babies to be born early and smaller.
Some women who have trichomonas infections do not have any signs. Men usually have no signs but they can carry it in the penis and pass it to a woman during sex.
Signs of trichomonas
- gray, yellow, or green discharge
- bad-smelling discharge
- red and itchy genital area
- pain during sex or burning while urinating
To help the woman feel better, she can sit in a pan of clean, warm water for 15 minutes as often as possible. This is soothing to the genitals and will speed healing. She should not have sex until she and her partner are finished with treatment and all the signs are gone.
| To treat trichomonas |  | ||||
| If the woman is pregnant: | |||||
| by mouth, 2 times a day for 5 days | ||||
| or | |||||
| by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days | ||||
| Also treat the woman’s partner with 2 g tinidazole or 2 g metronidazole by mouth, 1 time only. | |||||
Yeast (candida, white discharge, fungus)
Yeast is not usually sexually transmitted, but it is a very common vaginal infection. It is especially common in pregnant women or women who are taking antibiotics or birth control pills. Men can also get yeast infections.
Signs of yeast
- itchy genitals
- white, lumpy, sticky discharge
- bright red skin outside and inside the vagina that sometimes bleeds
- a burning feeling when urinating
- a smell like mold or bread dough from the vagina
Treatment
Yeast is not dangerous, but it is best to treat yeast in a pregnant woman before the birth, or the baby can get thrush. Mild yeast infections will sometimes go away without medicines. Rinsing with or sitting in a pan of warm clean water may reduce itching. Do this 2 times a day to feel better.
If a yeast infection does not go away on its own, try one of these medicines: icines:
| To treat yeast infection |  | ||||
|
high in the vagina, each night for 14 nights | ||||
| or | |||||
|
high in the vagina, each night for 6 nights | ||||
| or | |||||
|
high in the vagina, 1 night only | ||||
Prevention
Wearing loose clothing and underclothes made of cotton rather than polyester or nylon lets air around the genitals. This helps prevent yeast. Wash or change the underclothes often. Do not put soap in the vagina when bathing. Do not douche.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV, gardnerella)
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is not sexually transmitted, but when sex irritates the vagina, it makes getting this infection more likely. BV can cause pregnant women to have their babies too early. Many women who have bacterial vaginosis do not show signs.
Signs of bacterial vaginosis
- more discharge than usual
- a bad, fishy smell from the vagina, especially after sex
- mild itching
| To treat bacterial vaginosis |  | ||||
|
by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days | ||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 2 times a day for 5 days | ||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days | ||||
| Also treat the woman’s partner with 2 g metronidazole or 2 g tinidazole by mouth, 1 time only. | |||||