Hesperian Health Guides
Women’s health can damage or protect children’s hearing
HealthWiki > Helping Children Who Are Deaf > Chapter 15: Why children lose their hearing and what we can do > Women’s health can damage or protect children’s hearing
It is important that girls and women, especially pregnant women, have enough good food and access to health care. A baby can be born with hearing loss because:
- his mother was sick or did not eat well as a young girl, or during her pregnancy. For example, a baby born to a mother who did not get enough to eat can often be born early or have low birth weight and his hearing can be damaged.
- sickness or poor nutrition caused problems during birth. For example, if a woman has a small pelvis from poor nutrition, her baby may get stuck during birth. This could cause hearing loss from brain injury.
- some infections can pass from the mother to the baby during pregnancy and damage the baby's hearing. These infections include rubella (German measles), tuberculosis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and syphilis.
Contents
Lack of iodine in the diet during pregnancy

Iodine is a mineral found in the soil and water—and in foods like liver, onions, egg yolks, seafood, and plants from the ocean. When a pregnant woman does not get enough iodine, her baby may be born with cognitive delay or other disabilities including deafness. In some places in the world, the soil contains very little natural iodine so vegetables and crops that grow in the soil also contain little iodine. In these places, swelling of the thyroid gland in the neck is common. This is called goiter. If many people in your community have this swelling, then everyone needs more iodine.
A child with iodine deficiency may have cognitive delay, be deaf or unable to speak, and have weak neck and leg muscles. Many children only have hearing loss, some weakness in the legs, and take longer to learn. But others may have noses with a flat wide base, squinting eyes, hair low on the forehead, puffy eyelids and face, and have physical problems such as growing slowly and being short.
Treatment:
Get medical advice as soon as you can. A medicine called thyroxine, if started in the first months of life, may help a child with iodine deficiency grow better, though it will not help a child hear better.
The whole community, including the affected child, needs iodine supplements, but this will not help any nerve or brain injury that has already occurred.
Prevention:
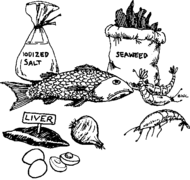
Goiter and iodine deficiency are easy and cheap to prevent. Women must get iodine before becoming pregnant. Taking iodine after the first few weeks of pregnancy is too late.
- The easiest way to get enough iodine is to use iodized salt instead of natural or rock salt. You can find packaged iodized salt in most places.
- Iodized oil taken by mouth is available in some countries. You need to take only 1 dose every 1 to 5 years.
- If iodized salt or iodine-rich foods are hard to get, you can make an iodine solution at home with Lugol's iodine. This is an antiseptic that is often available where medicines are sold.
To make an iodine solution to drink:
Rubella (German measles)
Rubella usually causes only a slight rash and gives the person no other problems. But if a woman who is pregnant gets rubella during the first 3 months of pregnancy, her child may be born deaf or with other disabilities.

Prevention:
- Give rubella vaccination to girls before they are old enough to have babies. If vaccination is not available, let young girls build a resistance to rubella before they are old enough to have children. They can visit people in the community who have rubella. They may catch the infection and develop resistance.
- If girls and women have not been vaccinated or have not had rubella by the time they are old enough to have children, they should prevent deafness in their babies, if they are or might be pregnant, by staying away from people with rubella.
Tuberculosis(TB)
Children of mothers who have tuberculosis during pregnancy sometimes get a type of meningitis called 'tubercular meningitis' in the first few months of life. This can cause deafness.
Prevention:
- Immunize children against tuberculosis with the BCG vaccine.
- Everyone, especially children, should get enough nutritious food so they stay healthy and can fight infections.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that can also pass to a baby during pregnancy. Untreated syphilis can affect many parts of the body. It can damage the inner ear and the nerves that affect hearing and cause deafness.
Signs:
Many babies born with syphilis do not have symptoms. Those that do may have jaundice (yellow skin and eyes), runny noses, rashes (often on palms and soles), swollen bellies, and enlarged lymph nodes. Children who develop symptoms after 2 years of age may have vision loss, hearing loss, cognitive delay, and abnormal tooth development. Some of these signs are different from those in adults.
Anyone who may have syphilis, including children, should see a health worker right away for testing and treatment. Everyone who is pregnant should get a blood test to check for syphilis. If the person cannot go to a health center or hospital to be tested, give the treatment for syphilis (see the box below).
| To treat syphilis in a child 1 month of age or less | |||
|
Inject slowly into the muscle 50,000 Units per kg of body weight, 1 time only. Do not give more than 2.4 milion Units in each dose. |  |
|
| or | |||
|
Inject slowly into the muscle 50,000 Units per kg of body weight, 1 time each day for 10 days. Do not give more than 2.4 million Units each day. |  |
|
| or | |||
| If the child is allergic to penicillin | |||
|
Give 62.5 mg by mouth, 2 times a day for 14 days. |  | |
| To treat syphilis in a child older than 1 month of age | ||||
| If the child tests positive for syphilis but has no symptoms: | ||||
|
Inject slowly into the muscle 50,000 Units per kg of body weight, 1 time each week for 3 weeks. Do not give more than 2.4 million Units in each dose. If the child has syphilis symptoms: |  | ||
| or | ||||
|
Inject slowly into the muscle 50,000 Units per kg of body weight, 1 time each day for 10 days. Do not give more than 2.4 million Units each day. |  | ||
| If the child has had syphilis for more than 1 year: | ||||
|
Inject slowly into the muscle 50,000 Units per kg of body weight, 1 time each day for 10 days. Do not give more than 2.4 million Units each day. |  | ||
| and | ||||
|
Inject slowly into the muscle 50,000 Units per kg of body weight, 1 time only, after course of procaine penicillin is complete. Do not give more than 2.4 million Units in each dose. |  | ||
| If the child is allergic to penicillin: | ||||
|
Give 7.5 to 12.5 mg per kg of body weight by mouth, 4 times a day for 30 days. |  | ||
| If the child is allergic to penicillin and is age 8 years or more: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2 mg per kg by mouth, 2 times a day for 30 days. Do not give more than 100 mg each time. |  | ||
| or | ||||
|
7.5 to 12.5 mg per kg by mouth, 4 times a day for 15 days. Do not give more than 250 mg each time. |  | ||
| To treat syphilis in an adult | ||||
| If the person has had syphilis less than 2 years | ||||
|
inject 2.4 million Units in muscle, 1 time only |  |
||
| or | ||||
| If the person is allergic to penicillin: | ||||
|
give 500 mg by mouth, 4 times a day for 14 days |  | ||
| or | ||||
|
give 2 g (2000 mg) by mouth, 1 time only |  | ||
| If the person has had syphilis for 2 years or more, or if you don’t know how long the person has had syphilis | ||||
|
inject 2.4 million Units in muscle, 1 time each week for 3 weeks |  |
||
| or | ||||
| If the person is allergic to penicillin: | ||||
|
give 500 mg by mouth, 4 times a day for 30 days |  | ||
To cure syphilis completely, the full treatment is essential.
Hearing loss caused by syphilis may develop when the child is an infant, or later as a teenager. Treating syphilis will not fix any hearing loss that has already occurred, but it will prevent any hearing loss that could still be caused.
See the books Where There Is No Doctor or Where Women Have No Doctor, published by the Hesperian Health Guides, for more information about syphilis.
Note: If a child is born with syphilis, the child's mother and father will also need treatment.
Cytomegalovirus
Most people with cytomegalovirus (CMV) are not sick. But babies of mothers who become infected during pregnancy can have severe deafness, blindness, or physical and mental disability. The germs that spread CMV can be found in body fluids—like saliva, urine, stool, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. To prevent the spread of CMV, wash hands with soap and water, especially after contact with stool, urine, or saliva.
Brain injury during birth can cause hearing loss
IIf a baby’s brain is injured during labor or birth, he may be born deaf. The baby's brain can be damaged if there is not enough oxygen reaching it. This is more likely to happen if labor is very long, if the baby is in a difficult position for birth, or if there are twins.
To prevent brain injury during birth
Midwives and others caring for pregnant women can learn about the danger signs during pregnancy and labor when a woman must get medical help at a hospital. Community members can organize to make sure there are ways to get women to the hospital if there is an emergency.

- Some methods to make labor go faster can injure the baby's brain, which can cause deafness. To protect the baby, avoid these ways to make labor go faster:
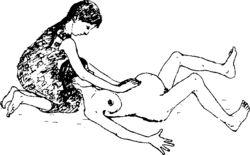 Do not push forcefully against the womb.
NO! |
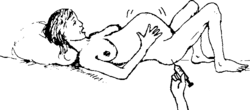 Do not give injections that make labor go faster.
NO! |
- Get medical help right away if the labor is taking too long, if the baby is in a difficult position, or if the cord is around the baby's neck. For more information about safe birth, see A Book for Midwives.


