Hesperian Health Guides
Allergies
Many things in the home can cause allergies, such as cleaning products, chemicals in carpeting and furniture, mold, pollen, animal dander, feathers, waste, dust and dust mites, cockroaches, rats, mice, and other pests. Exposure to toxics can lead to Multiple Chemical Sensitivity (MCS), which is similar to allergies. Some ways to prevent allergic reactions are:
- Improve the flow of air through the house.
- Reduce contact with the pollutant causing the allergic reaction.
- Keep the house clean and free of dust.
Contents
Dust and dust mites
Dust mites are tiny, invisible bugs that are the biggest cause of indoor allergies. They irritate the eyes and nose and cause asthma attacks. Dust mites live in warm, humid places filled with dust such as bed pillows, mattresses, carpets, stuffed toys, clothing, and furniture.
To get rid of dust and dust mites
Cleaning sleeping areas and bedding will help reduce dust, dust mites, and animal hair. Covering mattresses and pillows with tightly woven fabrics or plastic, and washing these covers in hot water regularly will help get rid of dust mites. If someone in the home is allergic to dust or dust mites, you may want to avoid having carpets, rugs, or other fabrics in the home.
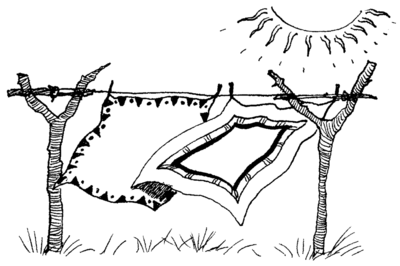 |
| Regular cleaning and airing materials outside in the sun will help to get rid of dust and dust mites. |
Mold
Mold is a kind of fungus, a simple plant that grows on soil and other plants. In the home, it grows on walls, clothing, old or spoiled foods, and in any damp place. Mold is also called ‘mildew.’ Most molds and mildews look like black or yellow powder, tiny threads, or white and blue fuzz.
Outdoors, molds are important to the environment. Molds help dead things decay and turn back into soil. But mold releases tiny spores that can cause health problems for people who breathe them. Molds also destroy the things they live on, so having mold inside the home is never good.
Molds cause breathing problems, headaches, skin irritation, and can trigger asthma attacks and allergic reactions. Rarely, exposure to some molds may lead to serious health problems and death, especially in infants. People with HIV are especially vulnerable to the health problems caused by molds.
To prevent and get rid of mold
Molds grow in damp places with poor ventilation. To prevent and get rid of mold, try to do 1 or more of these things:
- Fix leaks in walls, roofs, and pipes.
- Improve ventilation. When more air passes through the home, it keeps everything drier and helps prevent mold from growing.
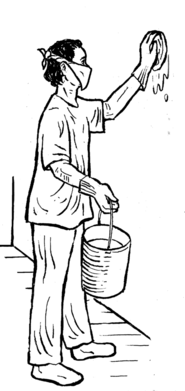
- Wash areas where molds grow with bleach solution.
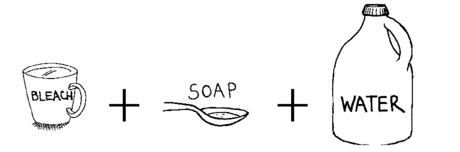
How to make a bleach solution
| Mix: 1 cup of bleach, ¼ teaspoon of liquid soap, and 4 liters (1 gallon) of water | |
|
|
 |
(Adding one cup of vinegar will help this solution kill more germs along with the mold.) |
Wear gloves and a face mask or cloth over your nose and mouth, and keep windows open while washing surfaces with this bleach solution. Let the solution stay on for 10 to 15 minutes, then rinse with plain water. Wipe the surfaces dry to prevent mold from growing back.


