Hesperian Health Guides
Chapter 15: The first weeks after the birth
In the first few days and weeks after the birth, the mother’s body will start to heal. Her womb should get smaller and stop bleeding. Her milk should come in. The baby should learn to breastfeed well and start to gain weight.
The mother and baby will still benefit from your care in the weeks after the birth. Visit them at least 2 times — the day after the birth, and then again at least once in the following week. If you visit even more, you may prevent more problems. Visit every day if there are signs of problems in the mother or baby.
Contents
What to do for the mother
Mothers need care after birth just as babies do, but they usually do not ask for it. Remind the family to help the mother heal after birth.
Help the mother care for herself
After birth, the mother's body is tired and her womb is open. It is easy for her to get infected, but she can stay healthy by:
- getting plenty of rest.
- eating a variety of nutritious foods.
- drinking plenty of fluids.
- staying clean — washing her hands, genitals, and breasts.
In some cultures, women rest in bed with their babies for 2 weeks or more after a birth. This is a healthy custom because it helps the mother heal, helps her and her baby to be closer, and keeps the mother away from germs outside of her home. If possible, the mother should not do difficult work for about 6 weeks. But she should be sure to walk around a little each day even if she is mostly resting.
Remind the woman and her partner that they should wait until the woman stops bleeding before they have sex. Also be sure to talk to the couple about family planning because the woman can become pregnant again soon.
Watch the mother's womb and bleeding
After the birth, the mother should bleed about the amount of a usual monthly bleeding or less. Her bleeding should stop after 2 or 3 weeks but may last as long as 6 weeks.
Her womb should be firm and get smaller and smaller each day.
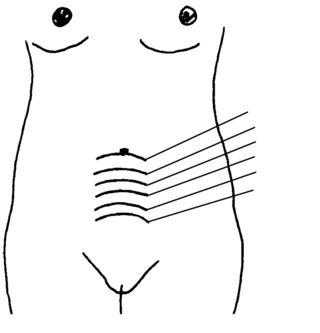
- Womb feels soft or large.
- Mother bleeds a lot.
- Mother has signs of shock.
The mother's womb
If the womb gets soft, rub it until it is firm. Show the woman's family how they can rub the womb when you are not there. Ask the mother to breastfeed more often, and watch for too much bleeding.
Also, feel the womb to be sure it is getting smaller. Just after birth, the top of the womb is about halfway between the pubic bone and the bellybutton. The next day, it is at the height of the bellybutton, and should be a bit lower every day after that.
The mother's bleeding
If the mother soaks more than 1 pad in an hour, she is probably bleeding too much. Rub the womb to help it contract. Remind the family that the mother needs to rest. Working too much often causes bleeding after a birth.
If these methods do not work, give medicines to stop bleeding. If the bleeding continues, or if the mother has signs of shock, get medical help right away.
Watch the mother for signs of womb infection
No fever — temperature around 37°C (98.6°F).
- Fever, 38°C (100.4°F) or higher
- Chills
- Fast pulse
- Heavy bleeding
- Bad-smelling genitals or bleeding
- Pains in the belly.
- An ill feeling.
If a woman has any of these signs after a birth, she may have a womb infection. Womb infections are very dangerous — they can quickly kill a woman.
If possible, a woman who may have a womb infection should go to a medical center right away. She can be tested to find out which antibiotic medicines will cure her infection. If you cannot get medical help, treat the woman at home.
Giving antibiotics at home
You cannot be sure which germs are causing a womb infection, so you will need to give 4 antibiotics to kill many different germs. If you do not have all of these antibiotics, it is better to give only 1 or 2 than none at all.
Give the antibiotics until the signs of infection have been gone for 2 days. This may take about 5 days altogether.
| To treat womb infection | |||||
|
in the muscle, then reduce the dose to 1 g (1000 mg), 4 times a day | ||||
| and | |||||
|
in the muscle, 2 times a day | ||||
| and | |||||
|
by mouth, 3 times a day | ||||
| Stop giving these antibiotics when the person has had no fever for 48 hours. Then start giving the antibiotics below. | |||||
| When fever has been gone for 48 hours: | |||||
|
by mouth, 2 times a day for 10 days | ||||
| and | |||||
|
by mouth, 3 times a day for 10 days | ||||
| or | |||||
|
by mouth, 3 times a day for 10 days | ||||
WARNING! If the woman does not start to feel better within 1 or 2 days, she may have pieces of the placenta still in her womb. These will need to be removed. Keep giving her antibiotics and take her to a hospital.
Watch the mother for signs of vaginal infection
Any tears in the vagina are healing, and the skin is not swollen or hot.
- Pain in the vagina
- Pus or a bad smell from the vagina
- Swelling, redness, or a hard lump in the vagina
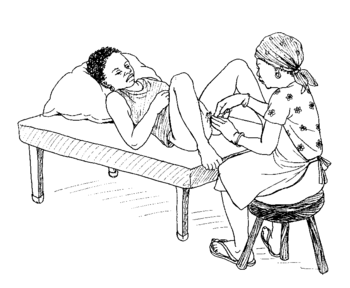
Wash your hands well, put on gloves, and look at the woman's vagina. If you see any of the warning signs listed here, she probably has an infection. If you see pus, check to be sure the pus is not coming from high inside her vagina. If it is, she probably has a womb infection.
If the pus is coming from a hard lump or tear on the woman's genitals, get medical help, or follow these instructions to drain the pus yourself.
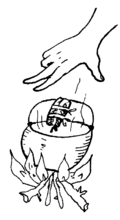
To drain the pus
Warm, wet cloths will usually draw out pus.

If the tear is open
Hold sterile cloths dipped in boiled warm water on the infected area.
If you know plant medicines that will draw out pus, wrap them in a sterile piece of cloth or gauze, and tie the cloth so the plants cannot fall out. Boil the wrapped plants, let them cool a little, and then press on the infected area.
If you feel a hard lump under the skin
If you feel a hard lump, pus or blood is probably trapped inside.
Watch the lump each day. If it is painful or growing larger, get medical help.
Watch for other warning signs
The mother's legs are red, hard, painful, or swollen
Very rarely after a birth, a woman’s blood will form a clot in her leg. Signs of a clot are:
- swelling or heat in one leg or foot.
- pain in one leg when it is squeezed or during walking.
- a painful red area on one leg.
- a hard lump in the leg.

woman's lung and make
breathing impossible.
A blood clot is very dangerous. If the clot breaks free and moves through her blood, it can cause problems in other parts of her body. For example, the clot can go into her lung and make it impossible for her to breathe.
If a woman has a sign of a blood clot, go to a medical center immediately. On the way, have the woman lie down with her legs above her hips and try to stay still. Put warm cloths on the swollen area, but do not rub or massage it. Give aspirin for pain.
Leaking urine or stool

leaking urine.
When urine or stool leaks all the time from the vagina, there may be a hole between the vagina and bladder or the vagina and rectum. This hole (a fistula) can happen during long, difficult labors when the baby’s head presses hard on the skin between the bladder and vagina or bladder and rectum for a long time. The pressure of the head is so great that the skin dies and a hole opens up there. This lets urine or stool leak out.
Fistulas can usually be treated and a small fistula may heal on its own. The woman should drink a lot of fluids and frequently sit in a shallow pan of warm water to relieve discomfort. If she is catheterized for 3 weeks, urine will be kept out of the fistula long enough for it to heal.
A large fistula or one that does not heal on its own needs to be repaired. There are hospitals that can do this surgery — usually about 3 months after the birth. Help the woman get to a medical center for help.
Fistulas can be prevented
A fistula happens when a woman is in labor for a long time. When a woman has
been in labor for many hours, do not keep waiting. Get medical help. Learn more
about preventing fistulas.
Give emotional support
It is important to give the mother emotional support. Customs and rituals that honor the mother or celebrate the birth are some ways to recognize the work and life changes that come with having a child.
What to do if the mother feels very upset or sad (depressed)
Most women feel strong emotions after giving birth. Some feel sad, worried, overwhelmed, or have little interest in things they usually enjoy. You can help by listening and letting her (and her family) know that these feelings are common. Help her find more support.
When these feelings are very strong, or last for more than 2 weeks, it is called depression. A woman who is depressed often needs help caring for herself, her home and family, and she needs help to stop feeling so down.
Encourage her family to watch the baby so she can rest. Moving and a little activity each day can help her mood and her sleep. Make sure she has nutritious food to eat and connect her to help if she does not. If traditional rituals and remedies are used in your area, explore these as well as modern medicines. Medicines for depression help some people but they do not work for everyone.
Women are more likely to experience these feelings if they have other life stress (like worries about money), if they did not plan to become pregnant, and if they had feelings like this after a previous birth.


