Hesperian Health Guides
Safe water
HealthWiki > Workers' Guide to Health and Safety > Chapter 29: Access to safe water and toilets > Safe water
If you do not have to pass urine during the day, or you pass only a small amount of urine, you need to drink more water. Other signs of not drinking enough water are:
- thirst
- headache
- feeling weak or dizzy
- bladder or kidney infection
- nausea
- muscle cramps
- dark-colored urine
- stomach pain
If you work in a hot climate or near hot machines, or if working makes you sweat, you should drink liquids whenever you are thirsty to prevent heat stress. Pregnant women need to drink even more. For more information about health problems caused by heat, see Chapter 15: Heat and cold. For more information about pregnancy, see Chapter 26: Reproductive and sexual health.
Drinking water is the best way to give your body the liquid it needs. Less liquid stays in the body if you drink tea, coffee, alcohol, or cola drinks. So drink plenty of plain water.
Safe drinking water and clean cups should be available in every work area. The water container should be clearly labeled. If the factory is very hot, the water must be kept cool.
Because illnesses such as colds and flu can be passed from one person to another if you drink from the same cup, the factory should provide clean cups. Wash used cups after every use with warm water and soap or bleach (1 part bleach to 10 parts water), and rinse with clean water.
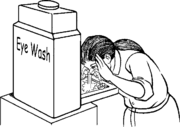
Water for first aid
Emergency showers and eye washes are necessary in areas where chemicals are used or stored. These first aid systems must provide clean, running water for at least 15 minutes. Running clean, cool water over a body part that is burned or has come in contact with a chemical is one of the best ways to reduce pain, lessen damage to a person’s body, and restore their health (see First aid when a chemical touches your skin or eyes). If there is too little water, this treatment may not work.
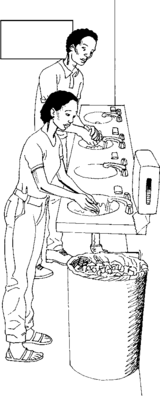
Water for washing hands
STATION
All workplaces should have areas where workers can wash their hands with clean water and soap. Washing hands with clean water and soap prevents illness from spreading, can keep wounds or burns clean, and removes chemicals.
Water for washing hands should be available near the toilets. There should also be clean water for hand washing in the work area for workers to wash their hands before going to eat or after working with any materials or chemicals. Areas for hand washing should be labeled and away from anything that might contaminate the water. All areas for handwashing should have soap.
Hand washing is especially important if you handle lead, dyes, or solvents, even if you wear gloves.
Do not use solvents to clean your hands. Use only soap and water.


