Hesperian Health Guides
Prevent and Manage Complications from Diabetes
HealthWiki > New Where There Is No Doctor > Diabetes > Prevent and Manage Complications from Diabetes
Contents
Take care of your feet
Good foot care is one of the most important concerns for people with diabetes. Nerve damage caused by diabetes can lead to loss of feeling (numbness) in the feet, making it hard to feel injuries. Diabetes also makes it harder for wounds to heal, easily leading to infection. Fungus on the feet (see Skin problems, in development) can also lead to infection.
A foot infection can spread to the whole leg if not treated. The leg may become so infected that a part of it needs to be removed (amputated). But good foot care and managing your blood sugar levels can prevent amputations.
Check your feet daily
It is hard to notice an injury that you cannot feel. So if you notice parts of your foot are becoming numb, be sure to check your feet by sight and touch every day. If you cannot do it by yourself, have someone help you. Some people use a mirror to see the bottom of their foot. Look for blisters, redness, cuts, or sores. Feel for warm or swollen areas, which can be early signs of infection. Make sure to also check between the toes.
Seek medical care for any wounds that do not heal or areas that stay red, warm, or swollen. It is important to treat wounds early to avoid serious complications.
Care for foot injuries
Keep injured areas clean and dry. Stay off the foot as much as possible. Use crutches for walking to lessen the pressure on the sores.
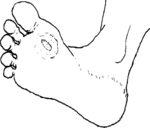
Ulcer |
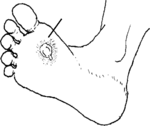
Infected Ulcer |
Clean sores with clean water or an antiseptic. Remove any dead tissue. (Dead tissue will feel cool to the touch and be darker in color.) Soaking the foot in warm (not hot) water can help remove dead tissue. Apply an antibiotic ointment and cover the sore with gauze or a clean, soft cloth. Put padding over it.
Watch for signs of infection, such as swelling, hardness, heat, or red lines going up from the wound. Treat infections with an antibiotic such as tetracycline, doxycycline, penicillin, or metronidazole.
If sores do not heal with self-care and rest, get medical help.
Prevent foot injuries
Wear shoes or sandals, even indoors. You might step on something sharp and not feel it.
Wash feet daily and pat dry. Always dry between the toes.
Always check inside shoes with your hands to make sure there is nothing sharp or rough inside before putting them on. Anything rough should be padded or clipped away.
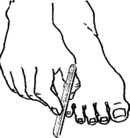
Toenails
An ingrown toenail can cut into the skin and cause infection. If a toenail is becoming ingrown, wedge a piece of wet cotton under the corner of the nail to help lift it out. Trim toenails straight across, being careful not to injure the toe, or use a file to keep them from becoming too long. Cutting them straight across instead of on a curve can help avoid ingrown toenails.

Check blood pressure
Everyone with diabetes should be checked for high blood pressure and everyone with high blood pressure should be checked for diabetes. Like diabetes, high blood pressure causes damage to the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, and other parts of the body. So if you have both diabetes and high blood pressure, the chances of developing heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, or other serious problems are greater than having either diabetes or high blood pressure alone.
A normal blood pressure is less than 140/90 mmHg. If blood pressure is high, try to lower it by increasing physical activity, reducing stress, and eating healthier food. These same changes help both diabetes and high blood pressure.
Medicines called ACE Inhibitors lower blood pressure and may protect against kidney failure. Another group of medicines called statins helps reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood, to make heart problems or a stroke less likely for people with diabetes. For more on medicines that lower blood pressure and cholesterol medicines, see the chapter Heart Disease and High Blood Pressure.
Stop smoking
People who smoke get diabetes more often, and people with diabetes who smoke have more serious health problems than those who do not smoke. Smoking tobacco damages more parts of the body than just the lungs. It blocks blood flow and raises blood pressure. Smoking is so harmful for people with diabetes that stopping smoking is even more important than lowering the sugar level in your blood. See Drugs, Alcohol, and Tobacco (in development) for help with how to stop smoking.

Vision
When blood sugar levels go too high, diabetes can cause blurred vision. This will usually clear up when the blood sugars have returned to normal. However, diabetes can also cause more permanent damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to gradual loss of vision or blindness. A person with diabetes should have their eyes tested once a year or more often if they already have some damage to their eyes. If damage to the blood vessels in the eye is detected early, it can be treated by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) to prevent loss of vision.

Mouth care
Diabetes worsens gum infections which, in turn, makes diabetes worse. People with diabetes should brush their teeth at least twice a day with a toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste or a chewstick (miswak, neem stick). If toothpicks or floss are available, use them to clean between the teeth. For more on how to prevent gum infections, see Teeth, Gums and Mouth (in development).
A person with diabetes will benefit from seeing a dentist. Always let the dentist know if you have diabetes.
Vaccines
People with diabetes should get regular vaccines to prevent diseases such as influenza and pneumonia, which can be more severe if you have diabetes.


