Hesperian Health Guides
Head Injuries
Contents
Signs of mild brain injury or concussion
- Confusion or loss of consciousness that gets better on its own in a short time
- Not remembering what happened
- Temporary blurry vision or “seeing stars”
- Nausea or vomiting that does not last long
- Headache, dizziness, or tiredness
Ask her to rest for about 24 hours and give paracetamol (acetaminophen) for the pain, but do not give ibuprofen or aspirin because they can worsen any bleeding inside the head. Watch the person for the first 24 hours. If she goes to sleep, wake her every few hours to see if she can still answer questions and think clearly. In the hours after the injury, if the person becomes more confused, gets a headache that gets worse and worse, or loses consciousness or has a seizure, there is likely bleeding inside the skull and immediate medical help is needed.
Signs of severe brain injury
Get help for any of these signs:
- Unconsciousness
- Severe or worsening headache, changes in vision, loss of balance
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion, personality changes, aggression
- Very slow, very fast, or changing (irregular) heart beat
- Fast, shallow breathing or breathing that is irregular (sometimes fast, sometimes slow)
- Warm, flushed skin
- Seizures
- Blood or clear fluid leaking from the ears or nose
These signs may happen hours after the injury:
- One pupil bigger than the other
 |
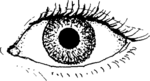 |
- Bruises around both eyes or behind the ear
 |
 |
Bleeding from the head
Head wounds bleed a lot. If you are sure the spine is not injured, ask the person to sit up, or prop her up, to decrease bleeding. Use pressure to stop the bleeding, then wash the wound well before closing it with sutures or glue. If you have no supplies you can tie the hair together across the wound, to help keep it closed, like this:
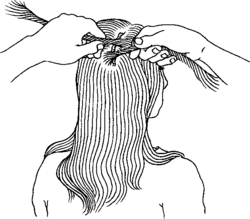
If the head is cut open, look for injury to the skull underneath. If you believe there may be an opening into the skull, apply pressure on each side of the wound and avoid pressing hard on the injured part of the head.
Nosebleeds

Pinch the nose firmly, just below the hard bony part.
Hold tight for 10 minutes — do not stop to check if the bleeding has stopped or the blood can start flowing again. If the nose still bleeds after 10 minutes, try pinching for another 10 minutes.
While most nose bleeds get better, any uncontrolled bleeding is dangerous. Beware especially of nose bleeds in old people.
Prevention
Rubbing a little petroleum jelly inside the nose might keep dryness from causing bleeding.
Nose picking is a common cause of nosebleeds.


