Hesperian Health Guides
Situations that affect breastfeeding
Contents
Twins
Twins should be breastfed just like other babies. Remember, the more a mother breastfeeds, the more milk her body will make. A mother can breastfeed both babies at the same time or she can breastfeed them one at a time.
A mother with twins will need more rest, food, drink, and help from her family and from you.
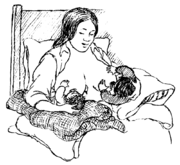 |
Two good positions for breastfeeding twins. |
 |
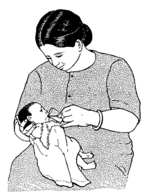
Small babies and early babies
Most small babies and early babies need breast milk. If the baby is too weak to suck from the breast, a mother can remove her milk by hand and then feed her baby with a cup or spoon until the baby is strong enough to breastfeed. Learn more about caring for small babies.

Breastfeeding while pregnant
It is safe to breastfeed while pregnant or to breastfeed an older child and a new baby. The mother should eat even more food and get plenty of rest.
The new baby should always be fed before the older baby.
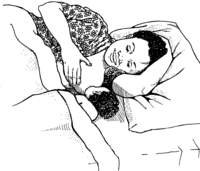
When the mother is sick
It is usually best for a mother to keep breastfeeding even when she is sick. To prevent becoming more sick, the mother can:
- drink plenty of fluids.
- lie down while breastfeeding.
Family members and friends can help the mother with her chores so she can rest.
Medicines
If possible, breastfeeding mothers should not take drugs or medicines. But some mothers who are sick must take medicines. These women should use medicines that are safe to take while breastfeeding.
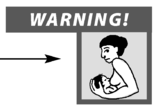
Most of the medicines listed in this book are safe to take while breastfeeding. A few that are not safe are marked with this symbol in the Medicines Pages.
HIV and breastfeeding
Someone who is breastfeeding should take special care not to become infected with HIV. Anyone who has HIV should start treatment as soon as possible to control their HIV. This protects the person's health, and the health of partners, and prevents HIV from spreading to babies during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Well-controlled HIV rarely spreads by breastfeeding.
Even without HIV treatment, breastfeeding only seems to spread HIV to 1 baby out of 3 who have HIV-positive mothers breastfeeding them. HIV seems to pass more easily during breastfeeding when:
- the mother was recently infected with HIV or is very sick with other infections. There is more HIV in the mother's body then.
- the baby is given formula or other fluids or foods as well as breast milk.
- the mother has cracked nipples or the baby has thrush in her mouth
In many places, breastfeeding is usually the safest way to feed babies even when mothers with HIV are not yet on treatment. This is because formula and other milks cause babies to get sick or die from diarrhea or malnutrition. Especially for mothers on treatment for HIV, more babies would die from formula than will get sick or die from HIV passed through breastfeeding.
To make breastfeeding most safe help women with HIV:

- Get on treatment for HIV and take it consistently. Be sure to give recommended medicines to the baby too.
- Give only breast milk for the first 6 months. Formula, teas, and other foods or drinks can irritate the baby’s digestion. And they have neither the nutrition nor protections against illness that breast milk does.
- If you have enough food to give your baby, make that the baby's main food after 12 months. But you can continue to breastfeed as long as the child wants to.
- Position the baby correctly for feeding to avoid cracked nipples.
- Treat thrush, cracked nipples, and breast infections right away.
- Women with HIV should not feed the baby from a breast that has mastitis or an abscess — instead, remove the milk and throw it away.
Heating breastmilk to prevent passing HIV
Breast milk can be heated almost to boiling to kill the HIV virus. A baby will not
be at risk of getting HIV from this heated milk. Heating breast milk takes
work, but it can be done if a woman has clean water, fuel, and support.
How to heat breast milk
| 1. Place a jar of breast milk in a pot of water. | Breast milk should not be boiled. |
| 2. Bring the water to a boil. | |
| 3. Immediately remove the pot from the heat. | Heated milk should be used within a few hours. |
| 4. Let the milk cool before feeding it to the baby with a cup or bottle. |


