Hesperian Health Guides
Women Face More Disease and Poor Health
HealthWiki > Where Women Have No Doctor > Chapter 1: Women's Health Is a Community Issue > Women Face More Disease and Poor Health
Not getting enough healthy food can keep children from growing properly and can lead to serious health problems.
Contents
Poor nutrition
Poor nutrition is the most common and disabling health problem for women in poor countries. Starting in childhood, girls are often given less food to eat than boys. As a result, they may grow more slowly and their bones may not develop properly. The problem worsens in early adulthood, because they need more good food as their workloads increase, and when they start having children. Yet women almost always eat last and least.
More Information
eating for good healthWithout enough healthy food, many women have poor health in general, including exhaustion, weakness, and anemia. When someone who is already malnourished becomes pregnant, they are more likely to have serious complications with childbirth, such as heavy bleeding, infection, too-long labor, or a baby that is born too small.

A woman’s health cannot be isolated from her social status. In most of rural India, women drink less milk than their husbands and sons, and they eat only after the men have been served. This usually leaves women with a limited diet, and it also tells about how she is valued.
CHETNA, Ahmedabad, India
Reproductive health problems
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV. Women are more likely to get infected with STIs for many reasons. With penis-in-vagina sex, the person with the vagina is more vulnerable to STIs because small tears can happen in the vagina. There is more risk with penis-in-anus sex, because the anus gets small tears even easier. Without a condom, semen stays inside the body after sex and can spread germs into the blood. The vagina may show no signs of infection from an STI, or the signs (for example, sores inside the vagina) may not be visible. So the person may not get treatment.
Without treatment, STIs can cause severe pain, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, problems during pregnancy, and an increased risk of cervical cancer.
Even more important, many women have little control over decisions about sex and often cannot refuse unsafe sex. As a result, millions of women get an STI every year, and more than 20 million are already infected with HIV.
|
Child marriage and frequent pregnancies. In many places, a third to half of young women become mothers before they are 20 years old. Without family planning, most do not have time to get strong again between births. This can lead to poor health and problems in pregnancy and birth. Frequent childbirth also means being less able to control your own life, get an education, and learn skills to support yourself.
One woman dies every 2 minutes from a problem related to pregnancy
Complications from pregnancy and birth. In recent years, fewer infants have died during or soon after birth. Yet every day, 810 women die from a problem related to pregnancy or childbirth. And for every woman who dies in childbirth, 20 to 30 more suffer from injury or infection. This means that over time, about a quarter of all women living in poor countries will be seriously affected by complications from pregnancy and birth.
Unsafe Abortion. Every day, more than 60,000 people try to end their pregnancies by seeking treatment from untrained persons or using unsafe methods. Without access to safe abortion services, many will die, be unable to have children in the future, or will be left with lasting pain, infection, and other health problems.
Female genital cutting. Female genital cutting, in which part or all of a girl’s outer genitals are cut off, can cause serious health problems. These include emotional trauma and ongoing problems, pelvic and urine system infections, pain during sex, and difficulties during and after childbirth. Despite these problems, about 4 million girls are at risk of being cut each year, mostly in Africa but also in parts of the Middle East, Asia, and places where people from these regions have migrated.
General health problems
Men and women get many of the same diseases, but women can be affected differently.
More Information
alcohol and other drugsWomen are more likely than men to have certain health problems because of poor nutrition, too little rest, or the type of work they do. A disease can also cause a different kind of harm to a woman than a man. For example, a disease that changes how a woman looks may make her husband or family reject her.
Although women get many of the same diseases as everyone else, they can be affected differently
Women's health problems are often taken less seriously than those of men. And when sick, women are less likely to seek and receive treatment until they are very ill. For example, tuberculosis (TB) spreads among everyone, but fewer women than men get treatment. Almost 1315 women die every day from TB—at least a third of them did not receive proper treatment or never even knew they had the disease. Some health problems that used to affect mostly men now affect women, too. For example, more women have problems from smoking cigarettes or drinking too much alcohol.
Work hazards

A woman faces health risks from her work inside and outside of the home. Working long hours, this “double work day,” can make her body less able to fight disease.
Women face health risks every day from their work. At home, heart and lung diseases from cooking-fire smoke (and burn injuries) are so common that they are considered the main workrelated health problem for women. Diseases spread through water are also common, because of all of the time women spend washing clothes, hauling water, or standing in water while farming.
Millions of women who work to earn money suffer health problems due to unsafe conditions and sexual harassment in the workplace. And when they come home from their jobs, they continue to work at home. This leads to exhaustion and an increased risk of illness.
Problems with mental health are as serious as other health problems.
Mental health problems
Women and men have about the same risk of developing a mental health problem. Severe depression, however, affects many more women than men, especially women who are poor, who have experienced loss or violence, or whose communities have been destroyed or undergone great change. Anyone with lower social status, or who feels they do not have a place in their community, may struggle with mental health problems.
When women suffer violence, it is usually from men they know. But most violence against women is not reported, and men are rarely punished.
More Information
rape and sexual violenceViolence
Violence is often overlooked as a health problem. But violence causes serious injuries, mental health problems, physical disabilities, and even death. Violence is also used to enforce inequality— for example, punishing someone who does not look or act appropriately as a man or a woman, or as a servant or child. Rape and sexual harassment are a constant threat to all women, in the community, at work, and at home. Many girls are sexually abused by family members or friends. Many women are forced to have sex or are physically abused by their partners. Rape and sexual assault are common during wartime.
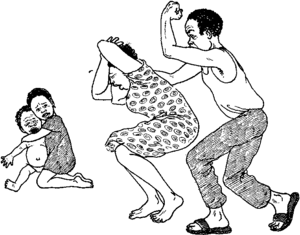
Even though this violence happens in almost all parts of the world, most of it is not reported, because the police and others often blame women and other targets rather than punishing the men.
Sources
- Hatcher, et al. (2018) Contraceptive Technology
- UNAIDS (2022) 20.2 million girls and women living with HIV
- UNFPA (2022) Maternal health
- Unicef (2021) 2 million additional cases of female genital mutilation likely to occur over next decade due to COVID-19
- UpToDate (2018) Screening for sexually transmitted infections
- World Health Organization (2019) Maternal mortality
- World Health Organization (2017) Worldwide, an estimated 25 million unsafe abortions occur each year



