Hesperian Health Guides
Physical Problems
Cerebral palsy (spastic child)
Cerebral palsy is a disability in the brain that affects the way a child moves and holds his body.
- At birth, the baby may be limp and floppy (but sometimes he seems normal at first).
- As the baby grows, he develops more slowly than other babies. He may be slow to hold up his head, sit, or crawl.
- The baby may have trouble feeding.
- He may fuss and cry a lot. Or he may be unusually quiet.
- As he grows, his movements are stiff and jerky.
About half of children with cerebral palsy are slower at thinking and learning, but do not assume this will be true. Children with cerebral palsy can play, learn, and go to school.
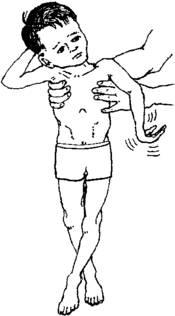
Cerebral palsy cannot be cured. But you can help a child with this disability move more on his own, communicate, and care for himself and others. Seek help from a clinic that provides rehabilitation or physical therapy, and see Disabled Village Children for more information about caring for a child with cerebral palsy.
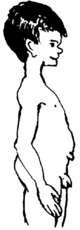

Belly button sticking out (umbilical hernia)
A belly button that sticks out like this is caused by a small separation of the belly muscles. They usually close on their own, and no medicine is needed.Tying a cloth or belly band around it will not help. (But after the cord falls off, it will not hurt either.)
Even a big umbilical hernia like this is not dangerous and will often go away on its own. If it is still there after age 5, get medical advice. Surgery may be needed.
Swollen testicle, hydrocele, and hernia
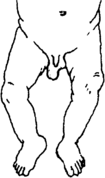
The bag that holds the testicles, called the scrotum, can fill with fluid or a loop of intestine. This causes swelling on the affected side.
You can find the cause of the problem. Shine a light from the back of the scrotum.
- If it shines through, the scrotum is filled with liquid. This is called hydrocele and will usually go away on its own. If it lasts more than a year, get medical advice.
- If the light does not shine through and the swelling gets bigger when the child coughs or cries, a loop of intestine (gut) has slipped in. This is called a hernia.
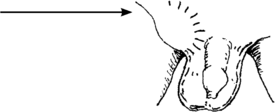
A hernia needs to be repaired with surgery. You may be able to push it back first:
- If possible, give diazepam to calm the child.
- Use pillows, or prop up the bottom of a bed or mat to get the child’s hips higher than his head.
- Have him bend his knee and open his leg on the side where the hernia is – like a frog.
- Put a cold compress or ice wrapped in cloth on the hernia to reduce swelling. Wait 10 minutes or more.
- If this doesn’t work, you can try gently and very slowly pressing the hernia back into place.
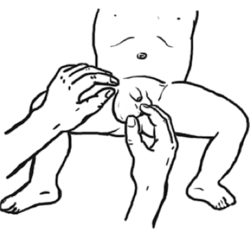
The child will still need surgery, even if you have pushed the hernia back into place.
Severe pain in the scrotum, especially if it starts suddenly, is usually a twist of tissue inside the body. This is called testicular torsion and the boy will need surgery right away to save the testicle.


