Hesperian Health Guides
Treating Harm Caused by Chemicals
HealthWiki > A Community Guide to Environmental Health > Appendix A: Safety and Emergencies > Treating Harm Caused by Chemicals
Chemicals can spill on the skin and clothes, splash in the eyes, or be swallowed or breathed in as fumes. If someone is hurt, get medical help as soon as possible.
Breathing in chemicals
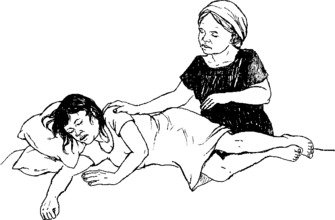
- Get the person away from the area where she breathed in the poison, especially if it is an enclosed area. If the spill happened indoors, open windows and doors.
- Get the person into fresh air.
- Loosen the person’s clothing.
- Sit or lay the person with head and shoulders raised.
- If the person is unconscious, lay her on her side and make sure there is nothing blocking her breathing.
- If the person is not breathing, do mouth-to-mouth breathing
- If there are signs of a health problem such as headaches, nose or throat irritation, dizziness, drowsiness or tightness of the chest. Seek medical help immediately. Take the chemical label or name with you.
Swallowing chemicals:
- If the person is unconscious, lay her on her side and make sure she is breathing.
- If the person is not breathing, quickly do mouth-to-mouth breathing. Mouth-to-mouth breathing can also expose you to the chemical, so cover your mouth with a pocket mask, or a piece of cloth or thick plastic wrap with a hole cut in the middle, before you start mouth to mouth breathing.
- If the person can drink, give her lots of clean water.
- Find the chemical package and read the label right away. The label will tell you if you should make the person vomit up the poison or not.
When chemicals spill on the body or clothing
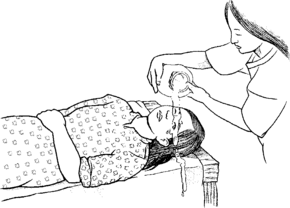
- If it is safe, first move the injured person away from the chemical spill.
- Remove any clothing, shoes, or jewelry the chemical spilled on. Be careful when removing pullover shirts or sweaters to prevent getting chemicals in the eyes. It may be best to cut the clothes off.
- Wash the affected area with cool water for at least 15 minutes.
- If chemicals got into the eyes, rinse with clean water for 15 minutes. Pull the eyelid away and move the eyeball in a circle so the entire eye is washed.
- If the person stops breathing, use mouth‑to-mouth breathing.
- Use a rag to soak up chemicals, being careful not to spread the chemicals around.
- If the body is burned by chemicals, treat them like ordinary burns.
This page was updated:05 Jan 2024


