Hesperian Health Guides
Burying Health Care Waste
HealthWiki > A Community Guide to Environmental Health > Chapter 19: Health Care Waste > Burying Health Care Waste
If there is waste collection and a landfill nearby, disinfected waste can be collected and safely buried there. If there is not, consider building small waste pits at the health center to make sure waste is safely buried. Because sharps are the most dangerous wastes, it is always best to bury needles and other sharp tools in a safe pit at the health center.
Burying waste is safest when everyone who handles the waste understands and follows the process.
Contents
Safe waste pits
For a waste pit to be safe, it should be located downhill from nearby wells, in an area where the groundwater is not near the surface, and at least 50 meters from rivers, streams, springs, and other water sources. Pit sides and bottoms should be lined with clay to prevent liquids from passing into the soil and groundwater. The pit should be well-marked and have a fence around it to keep people and animals out.
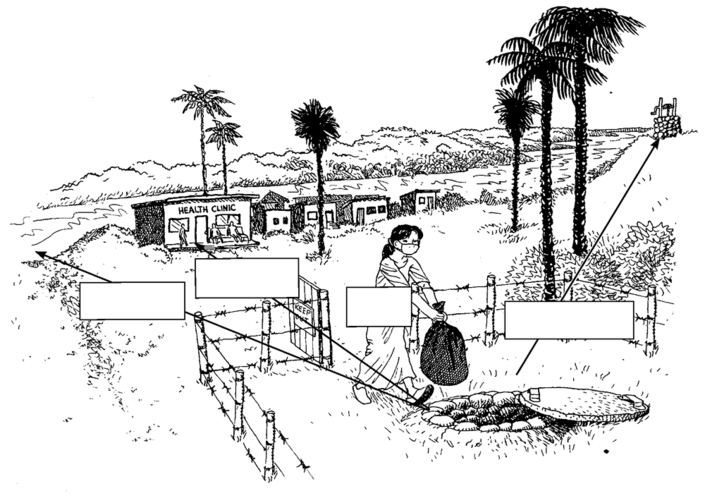
any water
buildings
gate
hill from a well
How to make a waste pit with a concrete cover
This kind of pit is best used only for infectious waste and not for regular garbage.
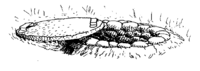
- Dig a pit 1 to 2 meters wide and 2 to 5 meters deep. The bottom of the pit should be at least 1½ meters above the highest level of groundwater (water table).
- Line the bottom of the pit with a layer of clay at least 30 cm thick.
- Build up a ridge of earth around the top of the pit to prevent surface water from running in.
- Build a fence around the area where the pit is located to keep children safe and animals out.
Each time waste is put in the pit, cover the waste with 10 cm of soil, or a mix of soil and lime. Lime helps disinfect the waste, and will also keep animals away.
When the waste rises to ½ meter from the surface, cover it with ½ meter of soil and seal it with a layer of concrete at least 10 to 30 centimeters thick.
How to seal sharps in containers with concrete
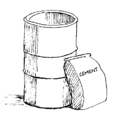
Place disinfected sharps and sharps containers in a hard container such as a metal drum. When the container is mostly full (¾), add a mixture of 1 part cement, 1 part lime, 4 parts sand, and ⅓ to ½ part water. Lime works as a disinfectant, and it also helps the cement flow into empty spaces to completely surround the waste. Seal the container and bury it in a trench or landfill.
Disposing of liquid waste
Many health centers pour bleach, contaminated water, or other liquids from the health center down a drain. This is only safe if the drain does not lead to a stream or other water source. Dilute the liquid with a lot of water before dumping it. To protect water sources, it is better to put used bleach and other liquids into a safe leach pit. Chemicals such as glutaraldehyde and formaldehyde should be treated before disposal.
To build a safe leach pit
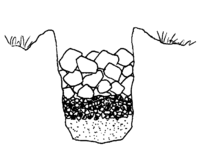
In a place where the ground does not flood, and far from waterways and wells, dig a pit ½ meter to 1 meter deep. In the bottom of the pit, put a layer of sand a few centimeters deep. Then put a layer of gravel a few centimeters deep, and a layer of larger stones on top. Put a cover on the pit to prevent rainwater from getting in.


